Exploring the Ecological Significance of Dingo Bones
Intro
Dingo bones offer a unique lens through which to examine not only the biological aspects of this species but also broader ecological and anthropological implications. Dingoes, classified scientifically as Canis dingo, have been an integral part of Australia's ecosystem since their arrival thousands of years ago. As researchers examine these remains, they uncover various layers of information that reveal significant insights into the evolution of canids, the interaction of species within their environment, and the sociocultural influences that surround these animals.
Understanding dingo bones can facilitate a deeper comprehension of multiple intersecting fields. This examination will explore the biological and ecological significance of these remains, their role in conservation efforts, and the cultural impact within Australian ecosystems. Consequently, this article aims to synthesize various research findings to provide a comprehensive resource tailored for students, researchers, educators, and professionals interested in biology, ecology, and anthropology.
Research Overview
Key Findings
Dingo bones have been pivotal in advancing knowledge in several areas:
- Evolutionary Insights: Analysis of dingo fossils has contributed to understanding the evolutionary history of canids and their adaptive strategies.
- Ecological Role: Dingoes help maintain ecological balance and species diversity within their habitats, acting as apex predators in many ecosystems.
- Conservation Significance: Investigations surrounding the preservation of dingo populations intersect with broader conservation efforts, given their importance in maintaining ecological integrity.
- Cultural Relevance: Dingoes hold symbolic and practical significance in Australian Aboriginal cultures, highlighting the intersection of natural history with human culture.
Study Methodology
To derive these findings, multiple methodologies have been applied:
- Archaeological Excavation: Field studies involving excavation of sites where dingo remains are found help to establish chronological frameworks.
- Osteological Analysis: The study of bone structure reveals age, health, and dietary habits of dingoes.
- Genetic Analysis: Advances in DNA analysis enable researchers to trace lineage and genetic diversity among dingo populations.
Background and Context
Historical Background
Dingoes are believed to have arrived in Australia approximately 4,000 years ago, brought by seafaring peoples. Their presence in prehistoric ecosystems marks a significant moment in Australia's evolutionary history. As part of the natural world, these creatures have adapted over millennia, significantly influencing the environment around them.
Current Trends in the Field
Recent studies focus on the impacts of human activity on dingo populations. Issues such as habitat loss, hybridization with domestic dogs, and their classification as pests in agriculture are under intense scrutiny. Researchers are exploring innovative conservation strategies to mitigate these threats. There's a growing recognition of the need to balance agricultural interests with ecological responsibilities. This involves understanding how dingo behaviors influence their ecosystems and the potential consequences of their decline.
"Dingoes play a crucial ecological role, maintaining system dynamics in ecosystems that would otherwise lose balance."
In summary, the examination of dingo bones offers significant insights into the biological, ecological, and cultural threads that make up the fabric of Australian life. This article serves as a comprehensive guide to the nuances of dingo remains, illuminating their importance in both past and present contexts.
Prelims to Dingo Bones
Understanding dingo bones is crucial for multiple fields such as archaeology, ecology, and conservation biology. The bones provide insight into the evolutionary history of canids, specifically the dingo as a unique subspecies of the domestic dog. This examination reveals how these animals have adapted to their environments and coexisted with humans over millennia. Moreover, the analysis of dingo bones addresses broader ecological dynamics and the implications for biodiversity in Australian ecosystems, which are under threat today. This section will serve as a foundation, highlighting the relevance and significance of dingo bones in various scientific studies and cultural contexts.
Definition and Background
Dingo bones refer to the skeletal remains of the dingo, scientifically known as Canis lupus dingo. These bones serve as valuable biological artifacts. They are critical for identifying the physical characteristics and health of dingoes over time. Bone structure includes aspects such as density, size, and shape. Understanding these facets aids researchers in reconstructing historical populations of dingoes. Studying dingo bones allows us to gather data related to their diet, lifestyle, and interactions with the environment.
Historical Context
Historically, dingoes have inhabited Australia for thousands of years. Their arrival is estimated at around 4,000 years ago, possibly brought by seafaring peoples from Southeast Asia. This adaptation to the Australian continent has led to an evolving relationship with the land and its other inhabitants. Dingo bones found in archaeological sites provide a tangible connection to these historical interactions.
These remains not only represent a part of the ecosystem but also reflect human behavior. For example, studies indicate that early Indigenous Australians may have utilized dingoes for hunting and companionship. Additionally, the dynamics between human settlements and dingo populations demonstrate how external factors influenced their distribution. This context is important for understanding current conservation efforts and the threats faced by dingo populations, including habitat loss and hybridization with domestic dogs.

Understanding the historical context of dingoes helps unravel their role in Australian ecosystems and their significance to Indigenous cultures and modern conservation.
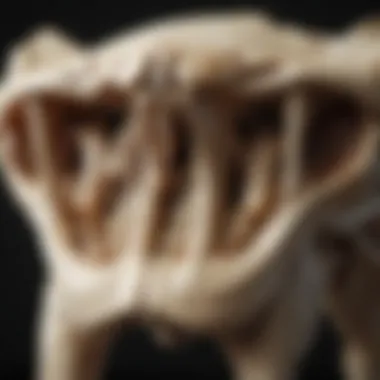
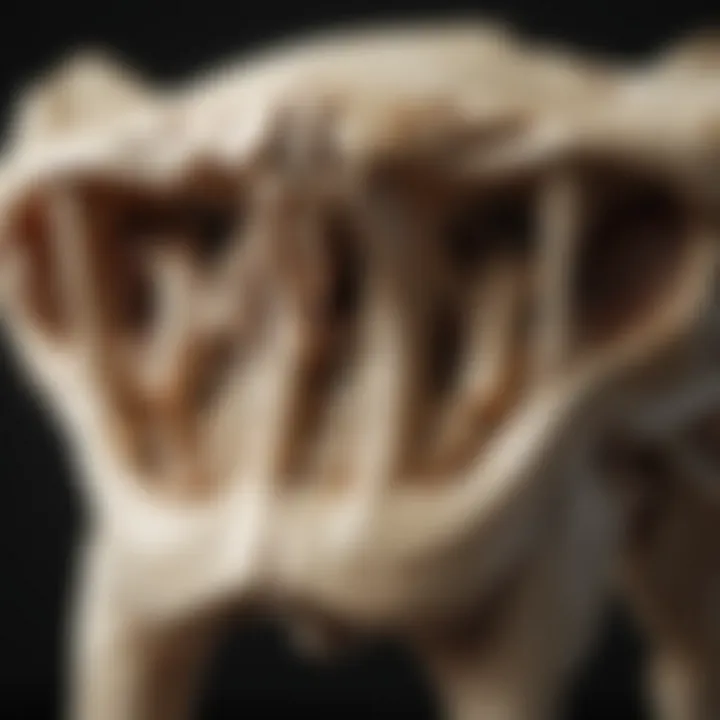
Anatomical Structure of Dingo Bones
The anatomical structure of dingo bones offers crucial insights into various biological and ecological aspects of this unique canid. By exploring the details of their bone composition, unique features, and comparisons with other canids, we can better understand the evolutionary adaptations and significance of dingoes in their environment. Understanding these aspects can serve as a foundation for further studies in fields such as zoology, conservation, and anthropology.
Bone Composition
Dingo bones are an important facet of their anatomy and play a vital role in their survival. The primary constituents of dingo bones include collagen and hydroxyapatite. Collagen is a protein that provides flexibility and strength, while hydroxyapatite gives the bones their hardness and structural integrity.
Additionally, dingo bones contain mineral salts, which contribute to their density. The balance of these components allows for a lightweight yet durable skeletal structure, enabling the dingo to be both agile and strong.
The variation in bone density provides insights into the lifestyle and habitat of dingoes. Bones from active adult dingoes, for instance, will show denser and stronger sections than those from younger or less active individuals.
Unique Features of Dingo Bones
Dingo bones exhibit several distinctive characteristics. One such feature is the elongated shape of their limbs, which allows for efficient running and hunting. The femur and radius bones are particularly adapted for speed and endurance, showcasing how evolutionary pressures have shaped their form.
Another key aspect is the robust construction of their skulls, optimized for powerful jaw muscles. This adaptation is significant as it enables dingoes to consume a diverse diet, which can include both large prey and smaller animals. The dental structure further reflects a carnivorous feeding habit, with sharp canines suited for grasping and tearing flesh.
Comparison with Other Canid Bones
When comparing dingo bones with those of other canids, such as wolves or domestic dogs, several differences can be noted. Dingoes exhibit a relatively smaller size and lighter bone structure compared to wolves, which aligns with their different ecological niches. Wolves, as larger apex predators, require stronger bones to support their size and hunting strategies.
Conversely, the bones of domestic dogs vary widely due to selective breeding, leading to diverse sizes and shapes. While some breeds may share similarities with dingoes, most have adaptations that serve human needs more than natural environments.
This comparative study highlights the significance of evolutionary adaptations in shaping the skeletal structures of canids, which reflects their ecological roles.
Ecological Role of Dingoes
The ecological role of dingoes is integral to the health of Australian ecosystems. As apex predators, dingoes maintain ecological balance by regulating prey populations. This regulation prevents overgrazing and ultimately supports biodiversity. Their presence impacts both flora and fauna, making them essential for a stable ecosystem. Understanding their ecological role gives insight into broader environmental management practices.
Dingo as a Apex Predator
Dingoes occupy the top tier of the food chain in Australia. This status allows them to control populations of various species, particularly herbivores such as kangaroos and rabbits. Without dingoes, there can be significant population booms of these herbivores. Such booms lead to overgrazing, which can devastate vegetation and degrade habitats. In turn, reduced plant life affects other species that depend on these plants for food and shelter. Therefore, the dingo's role as a predator contributes not just to the management of herbivore populations but also to the overall ecological integrity.
"Dingoes play a critical role in the health of their environment by controlling prey populations and influencing vegetation growth."
In addition to regulating prey species, dingoes also compete with other carnivores, such as foxes and cats, which are often viewed as invasive in Australia. The presence of dingoes can effectively limit these populations, which is crucial for protecting native birds and small mammals. Thus, their apex status contributes to a more balanced predator-prey dynamic, fostering a variety of life forms.
Impact on Biodiversity
The impact dingoes have on biodiversity is profound. By controlling populations of various species, they help maintain a balanced ecosystem. This balance ensures that no single species dominates, which could otherwise result in the decline of plant and animal diversity. Research shows that areas with healthy dingo populations tend to support richer biodiversity compared to areas where dingoes have been eliminated.
In diverse ecosystems, a healthy balance is paramount. Dingoes indirectly contribute to the survival of dozens of other species. Their hunting patterns create opportunities for other cohabiting species, reducing competition for resources like food.
Moreover, dingoes also play a role in nutrient cycling. As they hunt and consume prey, they leave behind remains that decompose and return valuable nutrients to the soil. This process encourages healthy plant growth, which supports a larger array of animal life.
Dingo Bones in Archaeological Studies


Dingo bones hold significant importance in archaeology, providing insights into the interactions between humans and dingoes over thousands of years. Through the analysis of these remains, researchers can uncover patterns that reveal shifts in human behavior, environmental changes, and the domestication processes of different canid species. Understanding these aspects is essential for constructing a comprehensive picture of Australian prehistory.
Methods of Excavation and Analysis
The excavation of dingo bones typically employs standard archaeological techniques, ensuring that bones are collected with minimal disturbance to their context. Stratigraphic layers are examined carefully, allowing for the assessment of the time frame during which the bones were deposited.
Once excavated, the analysis of dingo bones involves various techniques:
- Morphological Analysis: This method evaluates the shape and structure of the bones, helping to differentiate dingo remains from those of other canids. Specific measurements of the skeleton can indicate the size and health of the animals.
- Radiocarbon Dating: This allows researchers to determine the age of organic materials associated with the dingo bones. By dating the bones, archaeologists establish a timeline that aids in understanding the context of human-dingo interactions.
- Stable Isotope Analysis: This technique can provide information on the diets of dingoes and their ecosystems, revealing whether they hunted or scavenged food.
In combination, these methods provide a rich data set for understanding both the ecological role of dingoes and their relationship with humans through time.
Understanding Human-Dingo Interactions
Dingo bones found in archaeological sites often reflect a complex relationship with human populations. As apex predators, dingoes were integral to the ecosystems where they lived. Evidence suggests that they may have interacted with early humans in various ways:
- Hunting Practices: As hunter-gatherers, early Australians likely relied on dingoes both as competitors and as assistance when hunting for larger prey. The remains found may show evidence of butchery marks, indicating that dingoes were sometimes hunted for their meat.
- Cultural Significance: In many Indigenous Australian cultures, dingoes are not only seen as predators but as spiritual symbols or companions. Their bones may appear in ceremonial contexts or folklore, underlining their importance in human life.
"By examining dingo bones, we can discern the nuances of ancient human existence and ecological balance," says Dr. Emily Hartfield, an archaeologist specializing in Indigenous Australian studies.
Forensic Applications of Dingo Bones
Forensic science plays a key role in criminal investigations and legal processes. The study of dingo bones provides unique insights that can be valuable in forensic contexts. Dingo remains can help in the identification of canid species involved in incidents, particularly in areas where dingoes are present. Understanding the specific anatomy of dingo bones can assist law enforcement and forensic experts in distinguishing between dingo remains and those of other canine species.
Bone Identification Techniques
Bone identification techniques are crucial for correctly attributing remains to specific species. These methods rely on both morphological and genetic analyses. Morphologically, the size, shape, and unique features of dingo bones—such as the structure of the skull or the density of the long bones—are compared against established databases of canid bones.
Genetic analysis, including DNA sequencing, provides a more definitive means of identification. This technique is particularly useful in ambiguous cases where the untrained eye may struggle to discern between breeds or species. The extraction of DNA from bone samples can be challenging, yet advancements in technology have made it increasingly feasible, even from degraded samples.
Tools like x-rays and CT-scans are also employed to examine the internal structure of bones, revealing information about the bone's condition, any trauma, and time since death.
Case Studies Involving Dingo Remains
Several forensic case studies have showcased the applications of dingo bones in real-life scenarios. One notable case involved the examination of remains found near a national park in Australia. Forensic experts used bone identification techniques to confirm the remains belonged to a dingo, aiding in the investigation of poaching activities.
Another significant instance highlighted the identification of dingo remains found at a crime scene, where the presence of the bones raised questions about the role of local wildlife in specific criminal activities. This case demonstrated the importance of understanding the ecological context surrounding the evidence. By establishing the presence of dingoes in the area, investigators were able to develop clearer timelines and behavioral insights concerning local wildlife interactions.
The analysis of dingo bones in forensic cases not only contributes to solving crimes but also enhances our understanding of dingo behavior and ecology.
These cases exemplify how dingo bones are not just relics of the past but can provide critical evidence in solving contemporary issues related to wildlife and conservation. Overall, the study of dingo remains in forensic applications bridges the gap between biology, ecology, and justice.
Cultural Significance of Dingo Bones
The cultural importance of dingo bones cannot be understated. They represent not just remnants of an animal species but also signify a deep continuity with Indigenous Australian heritage and modern cultural interpretations. The bones of dingoes serve as a reminder of the ongoing relationship between humans and this unique species, shaping identities and traditions. Understanding this significance requires examining how Indigenous communities historically interacted with dingoes, as well as how these animals have permeated contemporary culture.
Role in Indigenous Australian Culture
For Indigenous Australians, dingoes are more than just wild animals. They play a prominent role in their cultural narratives and are central to local ecosystems. Traditionally, dingoes were often viewed as companions and helpers, assisting with hunting and in some cases even living alongside humans. Their presence in Dreamtime stories and lore highlights their spiritual importance. The bones from such animals often hold ceremonial relevance, being used in various rituals or as tools.


Furthermore, the practice of utilizing dingo bones in making implements or artworks demonstrates a sustainable approach to resource use, reflecting a respect for nature. The relationship with dingoes illustrates a mutual dependence, where the health of the dingo population can reflect the well-being of the land and the people dependent on it.
In a practical context, the remains of dingoes provide insights into the diets, hunting strategies, and material culture of Indigenous communities through archaeological findings. These findings contribute to a broader understanding of human-animal interactions in Australia across centuries.
Symbolism in Modern Contexts
In modern contexts, dingo bones symbolize multiple themes, including resilience and adaptation. As Australia experiences ecological changes, dingoes have been both vilified and celebrated as symbols of wildness. In artistic representations, dingo bones are often used to evoke themes of nature’s reclamation of human spaces.
In the environmental conservation movement, they symbolize the need for ecological balance and the importance of apex predators in maintaining healthy ecosystems. Awareness of this role is growing, leading to reinterpretation of dingoes not as mere pests but as crucial players in biodiversity. This shift is reflected in various media, where dingoes are depicted more positively, emphasizing their role in controlling prey populations and preventing overgrazing.
Dingo bones also find representation in discussions about cultural identity and heritage. There is a reviving interest in traditional practices, including the crafting and usage of dingo bone artifacts. This can lead to forms of expression that connect modern Australians with their history, culture, and the landscape they inhabit.
"Dingo bones serve as both historical artifacts and symbols of the enduring connection between Indigenous culture and nature."
The cultural significance of dingo bones weaves together the rich tapestry of past and present beliefs, practices, and ecological understandings. For students, researchers, and educators, exploring this aspect of dingo bones provides a comprehensive lens through which to view the intersections of biology, anthropology, and conservation.
Conservation Implications for Dingoes
Conservation implications for dingoes encompass a myriad of factors that are crucial for the survival of this iconic species in Australia. Understanding the threats they face and developing effective strategies for their conservation is vital for maintaining ecological balance and biodiversity. The significance of this topic lies in how it addresses the challenges encountered by dingoes while also highlighting potential avenues for preserving their population.
Threats to Dingo Populations
Dingo populations are currently under considerable threat from various sources. These threats can be categorized into both natural and anthropogenic factors. Some of the central threats include:
- Habitat Loss: Urbanization and agricultural expansion have significantly reduced the natural habitat available to dingoes. This encroachment disrupts their hunting patterns and leads to conflicts with humans.
- Hybridization with Domestic Dogs: One of the most concerning threats is the interbreeding between dingoes and domestic dogs. This hybridization dilutes the genetic lineage of traditional dingoes, undermining their distinct ecological role.
- Persecution by Humans: Misunderstandings about dingoes often lead to efforts to eradicate them due to fears regarding livestock predation. This negative perception feeds into local policies that fail to consider dingoes' ecological benefits.
- Disease: As dingoes come into closer contact with domestic animals, they face heightened exposure to diseases, which can negatively affect their health and population resilience.
Given these challenges, there is an urgent need for targeted conservation efforts to ensure dingoes can thrive in their native environments.
Strategies for Conservation
Effective conservation strategies are pivotal for addressing the threats faced by dingoes. Some of these strategies include:
- Habitat Restoration: Efforts should focus on restoring natural habitats that allow dingoes to hunt and live without interference. This can involve rewilding areas that have been significantly altered by human activities.
- Public Education and Awareness Campaigns: Educating the public about the ecological importance of dingoes can help mitigate negative perceptions. Programs aimed at informing local communities about the role of dingoes in the ecosystem may foster coexistence rather than conflict.
- Research on Hybridization: Ongoing studies monitoring genetic distinctiveness of dingoes are essential. Understanding the patterns of hybridization can guide policies that protect the integrity of dingo populations.
- Wildlife Corridors: Establishing wildlife corridors can help link fragmented habitats, allowing dingoes to migrate safely and secure their territories. This could also reduce roadkill and other risks associated with habitat fragmentation.
"Conservation is not just about protecting a species; it is about preserving the intricate web of life that they are part of."
Finale
The conclusion of this article offers a critical reflection on the multifaceted significance of dingo bones. It encapsulates the findings and emphasizes their importance not only in biological terms but also in ecological and cultural contexts. Dingo bones serve as valuable markers of evolution, revealing insights into the adaptation and diversification of canids over time. Understanding these aspects can significantly contribute to conservation strategies aimed at protecting the dingo population, which is increasingly threatened by human activities and habitat loss.
Summary of Findings
In summary, dingo bones provide substantial evidence in various fields of study. The article illustrates how these bones reveal critical information regarding:
- Anatomical structure: Dingo bones exhibit unique features that differentiate them from other canid species. Their composition offers insight into their dietary habits and ecological roles.
- Ecological impact: As apex predators, dingoes greatly influence biodiversity and ecosystem health in Australia. Their role in controlling prey populations plays a vital part in maintaining ecological balance.
- Cultural relevance: The exploration of dingo bones in indigenous Australian culture underscores their importance beyond mere anatomy. They reflect the relationship between humans and dingoes throughout history.
- Forensic applications: The techniques for identifying dingo remains enhance understanding in forensic science, broadening the scope of wildlife forensics.
This synthesis of findings illustrates the interconnectedness of biological, ecological, and cultural significances surrounding dingo bones.
Future Directions in Research
Future research into dingo bones could take several directions:
- Genetic studies: Analyzing genetic material from dingo bones can illuminate the evolutionary history and genetic diversity within the species.
- Impact of climate change: Investigating how changing environments affect dingo populations and their skeletal remains could provide insights into adaptability and survival strategies.
- Broader archaeological studies: Extending research methodologies to other regions may uncover new interactions between humans and dingoes, contributing to a wider understanding of their role in ecosystems.
- Conservation practices: A focused examination of dingo bones can lead to improved conservation measures that consider their ecological and cultural significance.
By pursuing these avenues, researchers can enhance the understanding of dingoes and foster more effective conservation efforts.







