Jaundice and Liver Cancer: Prognosis and Life Impact

Intro
Jaundice, marked by the yellowing of the skin and eyes, is a condition that often raises eyebrows. When it appears in patients with liver cancer, it signals more than just a symptom—it reflects underlying complexities of the disease. The connection between jaundice and liver cancer is multifaceted, encompassing not only clinical implications but also emotional and social dimensions that can profoundly affect patients' lives. This article endeavors to serve as a comprehensive guide to understanding these intricate relationships, emphasizing prognosis and quality of life.
Liver cancer, one of the more aggressive malignancies, can disrupt typical liver function, leading to conditions like jaundice. The appearance of jaundice can indicate liver dysfunction, often raising concerns about the individual’s health trajectory and treatment efficacy. As both medical professionals and the educated public grapple with this connection, understanding the prognosis becomes essential—not just in terms of survival statistics but also in the day-to-day realities faced by patients.
In dissecting this topic, we aim to evaluate current research trends and expert insights, drawing from various studies that identify key survival factors, treatments available, and their impact on the quality of life. Readers will find a detailed analysis of how these elements are interwoven, creating a rich tapestry of knowledge that reveals much about liver cancer and jaundice.
By exploring this intersection, we can expand our understanding of the disease, foster more empathetic healthcare, and ultimately, aid in navigating the stormy waters of liver cancer with a clearer perspective.
Foreword to Jaundice and Liver Cancer
The connection between jaundice and liver cancer is not merely a medical curiosity; it is a pivotal aspect of understanding patient outcomes and quality of life. Jaundice, defined by the yellowing of skin and eyes due to elevated bilirubin levels, can serve as a significant indicator of underlying liver dysfunction, including hepatic malignancies. For a patient grappling with liver cancer, recognizing the onset of jaundice can mean encountering a diverse set of complications that influence both survival rates and the overall experience of living with the disease.
Understanding this relationship provides critical context for healthcare providers and families navigating the treacherous waters of diagnosis, treatment, and long-term management. Liver cancer often devastates bodily functions, and jaundice can be an early warning sign that something is amiss within the liver— whether it be the cancer's direct effects or secondary conditions arising from the disease.
An informed grasp of jaundice types, its physiological mechanisms, and symptoms associated with liver cancer can not only enhance awareness but also drive proactive measures in terms of treatment and palliative care. Therefore, this section aims to highlight how these factors interconnect and outline their implications on patient prognosis and quality of life.
Jaundice in the context of liver cancer isn't just about what meets the eye; it reflects deeper, often complex physiological mechanisms at play and signifies the importance of timely medical interventions. Understanding these elements serves as a cornerstone for patients, caregivers, and clinicians alike, leading to informed decisions that could positively affect outcomes.
"Knowledge is half the battle— understanding the interplay between liver cancer and jaundice is crucial for navigating treatment pathways effectively."
As we delve deeper into the nuances of jaundice and its association with liver cancer, it becomes apparent that exploring these relationships offers vital insights. From the biochemical underpinnings to patient testimonials, every detail matters. The journey through this dialogue not only aims to raise awareness but also underscores the need for meticulous attention in patient assessment and management.
What is Jaundice?
Jaundice isn’t merely a medical term; it’s a vivid manifestation of underlying health issues, particularly in the context of liver cancer. Understanding jaundice holds significance as it provides insights into the severity of liver disease and can serve as a sentinel for potential complications. In a landscape where liver cancer can complicate prognosis, recognizing the implications of jaundice is vital for patients and healthcare providers alike. It invites a closer look not just at liver function but also at how this condition can affect a patient’s quality of life significantly.
Physiological Mechanism of Jaundice
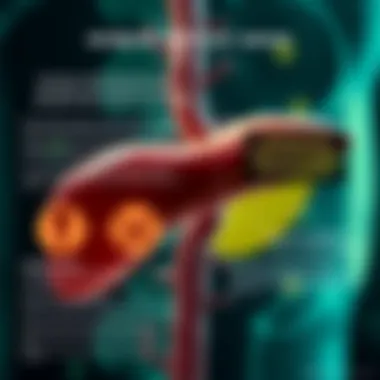
At its core, jaundice arises from an imbalance in bilirubin metabolism. Bilirubin is a yellow compound that is produced during the breakdown of red blood cells. When the liver is functioning optimally, it processes bilirubin and excretes it through bile. However, in conditions like liver cancer, this process is disrupted.
When the liver becomes impaired, bilirubin accumulates in the bloodstream, leading to the telltale yellowing of the skin and the whites of the eyes. There are three primary mechanisms through which jaundice manifests:
- Prehepatic Jaundice: This occurs prior to bilirubin reaching the liver, often resulting from excessive breakdown of red blood cells.
- Hepatic Jaundice: The liver itself is unable to efficiently process bilirubin due to damage (like that caused by liver cancer) or disease.
- Posthepatic Jaundice: This is a result of obstruction in the bile ducts, preventing the excretion of bilirubin.
Understanding these mechanisms not only helps in pinpointing the exact source of the problem but also informs treatment decisions.
Symptoms and Diagnosis
Recognizing jaundice involves observing clear signs and symptoms that may appear deceptively simple but can carry profound importance. Patients may notice:
- Yellowing of the skin and eyes
- Dark urine
- Pale-colored stools
- Itching
- Fatigue or malaise
While these symptoms can suggest jaundice, a proper diagnosis often requires a deeper dive. Medical professionals typically perform a combination of blood tests, imaging studies like ultrasound or CT scans, and sometimes liver biopsies to ascertain the root cause. These diagnostics not only establish the presence of jaundice but also reveal its connection to liver cancer, guiding treatment and management strategies.
Understanding jaundice in patients with liver cancer can simplify complex clinical decisions, highlighting the need for tailored intervention.
Liver Cancer: An Overview


Understanding liver cancer is pivotal when discussing the related complications like jaundice. Liver cancer is a serious health concern worldwide, and its ramifications are profound. Patients diagnosed with liver cancer need to navigate a plethora of challenges, both medical and psychological. This section serves as a foundation, offering insights into the types and stages of liver cancer, which are indispensable for comprehending how jaundice fits into the broader picture of this disease. By comprehending these elements, one can better grasp the potential impact of liver cancer on an individual’s life and the factors that may contribute to their prognosis and overall quality of life.
Types of Liver Cancer
Liver cancer is not a one-size-fits-all diagnosis; it comes in various forms, and each type demands its approach. The two most common types are hepatocellular carcinoma and cholangiocarcinoma. Hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC) is the most prevalent form, typically arising from cirrhosis related to factors such as hepatitis B, hepatitis C, and excessive alcohol intake. On the flip side, cholangiocarcinoma originates from the bile ducts—though it accounts for a smaller percentage of liver cancers, its implications are similarly dire.
It's crucial to recognize that the risk factors differ across these types. Factors that contribute to HCC may not necessarily apply to cholangiocarcinoma. For instance, chronic liver diseases are often cited as significant contributors to hepatocellular carcinoma, while obesity and certain genetic predispositions may increase risks for bile duct cancers.
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma
- Cholangiocarcinoma
- Arises from hepatocytes
- Commonly associated with chronic liver diseases
- Develops from the cells lining the bile ducts
- Less common but equally serious
This distinction is vital for understanding the broader implications of liver cancer, particularly concerning treatment decisions and monitoring for jaundice—a frequently occurring symptom in these patients.
Stages of Liver Cancer
The staging of liver cancer plays an essential role in determining the prognosis and available treatment options. Assessing how far the cancer has spread allows healthcare professionals to devise a tailored approach for patients. The most recognized staging system is the Barcelona Clinic Liver Cancer (BCLC) staging system, which stratifies liver cancer into stages ranging from very early to terminal.
- BCLC Stage 0: Tumors are small and confined to the liver.
- BCLC Stage A: Patients usually have a single tumor with good liver function.
- BCLC Stage B: Multiple tumors present but still confined to the liver.
- BCLC Stage C: Cancer has spread to nearby blood vessels or lymph nodes.
- BCLC Stage D: Advanced cancer, often with cirrhosis and deteriorating liver function.
Each stage is indicative of not just the cancer's severity but also its relatioonship with jaundice. Jaundice tends to become more pronounced as the disease advances, especially in stages C and D, profoundly affecting the individual's quality of life.
Epilogue of Overview
In summary, recognizing the types and stages of liver cancer lays the groundwork for understanding how jaundice manifests in these patients. As they navigate diagnosis and treatment, grasping these categories helps clarify the medical landscape they are facing and how it intertwines with symptoms such as jaundice. This understanding is not merely academic; it is critical for managing expectations and planning for a range of possible outcomes.
Relationship Between Liver Cancer and Jaundice
The interplay between liver cancer and jaundice is a crucial topic, particularly because jaundice often signals underlying issues in the liver, a critical organ for metabolism and detoxification. Understanding this relationship sheds light on the broader context of liver cancer, emphasizing the need for awareness about symptoms and overall patient care.
Jaundice occurs when there is a buildup of bilirubin, a yellow pigment formed from the breakdown of red blood cells. In patients with liver cancer, this accumulation can stem from multiple factors, including blocked bile ducts due to tumors or impaired liver function due to the cancer itself. Thus, examining how liver cancer affects bilirubin processing can provide insights into prognosis and quality of life.
Pathophysiology of Jaundice in Liver Cancer
The pathophysiology of jaundice in the context of liver cancer is multifaceted. As cancer progresses, the liver’s ability to produce bile and process bilirubin diminishes. Tumors can obstruct bile ducts, causing bilirubin to accumulate in the bloodstream. When bilirubin levels exceed a certain threshold, the characteristic yellowing of the skin and eyes is observed.
- Bile Duct Obstruction: Tumors in the liver can directly invade or compress bile ducts, leading to a significant reduction in bile flow. The resulting cystic dilation due to obstructed bile can further exacerbate jaundice.
- Liver Function Impairment: As liver cancer advances, the liver's functional capacity declines. Hepatocytes, or liver cells, become damaged, reducing their ability to metabolize and excrete bilirubin, contributing to jaundice.
- Intrahepatic Cholestasis: This condition is common in liver cancer, where the bile produced cannot effectively flow due to the structural changes in the liver caused by tumors.
These physiological changes not only signal the severity of the disease but also complicate treatment options, emphasizing the need for close monitoring and specialized interventions.
Incidence of Jaundice in Liver Cancer Patients
The incidence of jaundice in patients with liver cancer is notable and varies depending on cancer type and stage. Studies indicate that approximately 30% to 50% of patients with advanced liver cancer might experience jaundice as a symptom.
- Hepatocellular Carcinoma: This type of liver cancer, arising from liver cells, often sees higher incidence rates of jaundice, especially in advanced stages due to its aggressive nature and tendency to invade surrounding structures.
- Cholangiocarcinoma: This cancer, originating from bile ducts, frequently leads to jaundice even in early stages due to inherent obstruction of bile flow.
- Risk Factors: Individuals with underlying liver diseases, such as cirrhosis or hepatitis, are at an increased risk of developing jaundice when diagnosed with liver cancer.
It is clear that jaundice acts not just as a symptom, but as a potential indicator of cancer severity and an essential factor in patient management strategies.

Understanding the relationship between liver cancer and jaundice is vital for both prognosis and treatment. As medical professionals gain more insights into the underlying mechanisms, the hope is that early intervention can be prioritized, ultimately improving survival rates and patients' quality of life.
Survival with Jaundice: What the Data Shows
Understanding the connection between jaundice and liver cancer involves unpacking several layers of complexity. Survival rates are critical indicators that direct not only treatment decisions but also influence patient expectations and planning. Knowing how jaundice affects survival outcomes can help patients and healthcare providers strategize both immediate and long-term care paths. Additionally, in a broader scope, this data can inform clinical practices and encourage further research into liver cancer management and treatment efficacy.
Statistical Trends and Prognostic Factors
When we delve into the statistics surrounding liver cancer and jaundice, some patterns emerge that offer insights into prognosis. Research indicates that the presence of jaundice can be linked with a more severe stage of liver cancer, which often correlates with poorer survival rates. A variety of factors plays a significant role in shaping these statistics.
- Liver Function Tests: Bilirubin levels, a measure often associated with jaundice, can act as a prognostic indicator. Elevated bilirubin levels can signal disease progression, indicating a heartier cancer burden.
- Tumor Size and Type: The cancer's histology, or the microscopic characteristic of the tumor, greatly influences survival outcomes. Some types, like hepatocellular carcinoma, have different prognoses than others, and their interaction with liver function, as seen with jaundice, can alter survival predictions significantly.
- Patient Factors: Age, overall health, and comorbid conditions - such as diabetes or hypertension - can skew the results. Younger patients with less severe comorbidities show better survival rates, even in the presence of jaundice, compared to older patients with significant health issues.
These trends reveal how multifaceted the relationship is between jaundice and liver cancer, emphasizing that statistical insights must be personalized to individual patient circumstances for effective clinical decision-making.
Survival Rates by Cancer Stage and Jaundice Severity
Survival rates for liver cancer patients often depend heavily on the stage at which the disease is diagnosed. Specifically, levels of jaundice can be an indicator of stage and overall prognosis.
- Stage I: Patients diagnosed at this stage, often presenting with no jaundice, have a much higher five-year survival rate, which can be as high as 70–80%.
- Stage II: When patients begin to show mild jaundice, survival rates drop to around 50% over five years. This is largely due to the increased complexity of treatment options available and the potential for the cancer to spread beyond the liver.
- Stage III and IV: Jaundice becomes more prominent at these stages, correlating with severe liver dysfunction. The survival rate in Stage III hovers around 30%, while Stage IV can plummet to below 5%. Here, significant past studies reported data that promotes a pressing need for tailored treatment plans focused on managing jaundice and its implications.
"The prognosis of liver cancer coupled with the presence of jaundice underscores the urgent need for further research, as statistical trends bring clarity to individual treatment options, encouraging a more tailored approach in patient care."
For deeper insights and continuing updates on liver cancer research, one may find valuable resources at Britannica and community discussions on platforms like Reddit.
Quality of Life Considerations
The intersection of jaundice and liver cancer profoundly impacts the quality of life for affected patients. This section delves into the specific elements that contribute to this topic. Understanding how these two conditions interact is essential for both healthcare providers and the patients themselves, as the implications stretch beyond survival rates into the very fabric of daily existence and overall well-being.
Impact of Jaundice on Daily Life
Jaundice is not merely a symptom; it drastically alters the daily routines and lifestyle of individuals diagnosed with liver cancer. Patients often report a range of physical ailments that can impede normal activities.
- Fatigue: One of the most common complaints is overwhelming fatigue. This isn’t just a sense of tiredness; it’s a deep fatigue that can make even the simplest tasks feel like climbing a mountain.
- Skin and Eye Discoloration: The yellowing of the skin and eyes can be visually distressing, drawing unwanted attention and leading to feelings of self-consciousness.
- Dietary Restrictions: Many patients must alter their diets significantly, avoiding certain foods that may further burden their liver. This can lead to frustration and feelings of deprivation.
These factors coalesce to create a picture of daily life that is often laden with challenge. Patients may find themselves weighing the desire for social interactions against the physical and emotional toll that their condition imposes. Such decisions can lead to isolation, impacting their relationships with family and friends, and sometimes leading to depression.
"Quality of life is not merely about living longer; it’s about thriving despite adversity."
Psychological Effects of Diagnosis
The emotional toll of receiving a diagnosis of liver cancer, compounded by jaundice, is profound and often underestimated. For many, the journey starts with denial, spirals into anxiety, and can culminate in depression.
- Fear of the Unknown: Questions abound. What does this mean for my future? How will my life change? Such uncertainties can plague the mind relentlessly.
- Loss of Independence: With increasing health challenges, many patients experience a loss of autonomy. Relying on caregivers for daily activities can be disheartening, as this shift alters family dynamics and personal identity.
- Coping Mechanism: Psychological resilience plays a critical role. Some individuals might engage in support groups or therapy, whereas others might withdraw into themselves. Finding effective coping strategies becomes paramount.
As these psychological layers unfold, the interplay between mental health and physical symptoms becomes apparent. Healthcare providers must be aware of these aspects, addressing the full spectrum of a patient's experience. Understanding the psychological landscape not only aids in delivering better care but also offers patients a chance at regaining control over their lives, empowering them amidst the uncertainties of their diagnosis.
Medical Management of Jaundice Related to Liver Cancer
The management of jaundice in patients diagnosed with liver cancer is pivotal not just for prolonging life but also for enhancing the quality of life. The intersection between jaundice and liver cancer creates a complex clinical picture that necessitates careful evaluation and intervention. Jaundice itself often signifies an underlying dysfunction in the liver, potentially due to malignancy. Thus, effective medical management seeks to address both the symptoms of jaundice and the progression of liver cancer. The following sections delve into available treatment options and palliative care approaches to highlight their importance in managing this condition.


Treatment Options Available
When it comes to treating jaundice in the context of liver cancer, there are several avenues to explore, each catered to specific patient needs based on factors like the stage of cancer and overall health. Here are some pivotal treatment strategies:
- Medication: Some medications, such as corticosteroids, can help alleviate symptoms associated with jaundice. They might work by reducing inflammation around the liver or treating associated conditions that cause elevated bilirubin levels.
- Biliary Stents: For patients with bile duct obstruction, biliary stenting may provide immediate relief of jaundice symptoms. This involves placing a small tube in the bile duct to allow bile to flow freely, mitigating complications that arise due to liver cancer.
- Surgical Options: In certain cases, surgical procedures may be indicated. Resection of tumors or even liver transplant may become necessary, particularly if the cancer is localized and the liver function is still relatively intact.
- Chemotherapy and Radiotherapy: These treatment modalities can control the growth of liver tumors, consequently improving liver function and reducing jaundice.
While each treatment has its own benefits and risks, personalized care is essential. Tailoring the approach based on individual circumstances can lead to better management of the condition and improvement in quality of life.
Palliative Care Approaches
Palliative care plays a crucial role, particularly for those at later stages of liver cancer. The goal here is not to cure but to improve quality of life and manage symptoms effectively. Patients can benefit from:
- Symptom Management: This involves a comprehensive strategy to address symptoms like itching from the build-up of bile salts, pain management, and discomfort associated with ascites or fluid retention.
- Nutritional Support: Loss of appetite and weight can significantly affect patients. Nutritional counseling and support is vital, as maintaining strength can improve tolerance to treatments and enhance overall well-being.
- Psychosocial Support: Counseling and support groups can help patients and their families navigate the emotional challenges brought on by a liver cancer diagnosis. This holistic approach is integral to ensuring that patients feel supported throughout their journey.
The importance of integrating palliative care with regular treatment regimens cannot be overstated. It addresses not only the physical but also emotional, social, and spiritual needs of the patient.
Future Directions in Research
Research into jaundice within the context of liver cancer is like lighting a candle in the fog—it's essential for illuminating a notoriously complex area of medicine. Understanding the mechanisms behind jaundice and its interplay with liver cancer can lead to better patient outcomes and elevate the standard of care provided. With the increasing incidence of liver cancer worldwide, identifying innovative approaches for early detection and treatment is paramount.
Innovations in Early Detection and Treatment
Early detection is key in treating liver cancer effectively. Innovations in medical technology have presented promising new methodologies that could revolutionize how we approach this condition. For instance, advanced imaging techniques such as multi-parametric MRI and contrast-enhanced ultrasound are making waves. These methods allow healthcare professionals to visualize liver abnormalities much earlier than traditional imaging modalities would permit.
Additionally, liquid biopsy technologies have emerged as a significant development in cancer detection. These involve analyzing blood samples for circulating tumor DNA or RNA, enabling oncologists to detect cancer markers without invasive procedures. Early identification through these means can facilitate timely interventions, increasing the chances of favorable outcomes and tailoring treatment to individual patients’ needs.
Furthermore, various clinical trials are underway to explore novel therapeutic agents aimed at minimizing the effects of jaundice in liver cancer patients. A fine example is the exploration of novel hepatoprotective agents which might help mitigate liver damage due to both the cancer itself and standard treatments such as chemotherapy.
Potential for Personalized Medicine
Personalized medicine has gained traction in the past decade and holds immense promise for liver cancer treatment. This approach tailors medication and treatment methodologies based on the patient’s unique genetic makeup, lifestyle, and specific tumor characteristics. The idea is not one-size-fits-all; instead, it’s about crafting treatments that are curated specifically for the individual.
In the realm of personalized medicine, significant advancements are being made in identifying genetic markers associated with liver cancer. For example, research is currently delving into the genetic profiling of tumors to predict responsiveness to particular therapies—an approach that could allow healthcare providers to tailor their prescribing habits more accurately. This could reduce adverse effects and enhance therapeutic efficacy, ultimately improving both the prognosis and quality of life for patients dealing with liver cancer.
The potential of combining genetic insights with traditional treatment modalities is vast. Drugs like sorafenib and regorafenib can be optimized using genetic data, ensuring that only the most suitable patients receive them, thus avoiding unnecessary treatments for individuals unlikely to benefit.
"Innovation in research is not merely about new techniques; it's about rethinking our understanding of diseases and our approach to individual treatment."
In summary, future directions in the research of jaundice and liver cancer hold significant potential. Innovations in early detection and personalized medicine must be pursued avidly as they can significantly influence prognosis and enhance the quality of life for affected individuals. Understanding these aspects will not only advance medical knowledge but ultimately lead to improved patient care and outcomes.
Finale
Overall, discussing the connection between jaundice and liver cancer highlights critical aspects that are vital for both medical professionals and patients. Jaundice not only provides a window into the underlying dysfunction of liver health but also signals pivotal changes during liver cancer progression.
A thorough understanding of this relationship arms healthcare practitioners with the knowledge to tailor treatments and interventions to each patient's unique situation, ultimately optimizing care pathways and enhancing outcomes. For instance, knowing how jaundice can affect prognosis enables professionals to better communicate the possible trajectories of treatment and survival.
In addition, quality of life considerations emerge as equally crucial. As jaundice manifests, patients often endure not only physical symptoms but also emotional and psychological strains that stem from their diagnosis. Addressing these elements can lead to more comprehensive support strategies, ensuring that treatment addresses individual needs holistically.
"Awareness of the interplay between jaundice and liver cancer is key for fostering resilience and managing expectations for both patients and families."
By distilling research findings and clinical experiences into actionable insights, this article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers keen on understanding not only the science behind jaundice in liver cancer but also the broader implications on patient care. Being informed can empower decision-making and instill a sense of agency, even in challenging circumstances.
In this ever-evolving field of oncology, staying abreast of new data and treatment methodologies will continue to shape the narrative around liver cancer and jaundice, paving the way for improved survival rates and enriched life quality.
Thus, the conversation must persist; ongoing dialogue about the ramifications of jaundice amid liver cancer becomes essential in championing better health outcomes and quality of life for those affected.







