Osteonecrosis of the Jaw Incidence in Prolia Users


Intro
In recent years, the prescription of Prolia has grown, becoming a mainstay in osteoporosis management. However, alongside its benefits, there are serious considerations. Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) has surfaced as a notable risk linked to this treatment. Understanding the interplay between Prolia and ONJ is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers. This article delves into the incidence of ONJ among Prolia users, shining a light on risk factors, preventive measures, and vital recommendations for those managing patients.
Research Overview
Key Findings
The emergence of ONJ in patients receiving Prolia treatment has generated attentiveness within the medical community. Studies indicate that the incidence rate of ONJ in these individuals, while considered low, is still significant enough to warrant proactive measures. Research points out that patients with underlying risk factors—such as dental issues or prior therapies related to bone health—are particularly susceptible.
"Prolia, while effective for bone density, necessitates careful monitoring for jaw health."
Study Methodology
The analysis of ONJ incidence often relies on retrospective studies, meta-analyses, and patient case reviews. Many recent scientific efforts have focused on quantifying occurrences of ONJ while also scrutinizing the demographics most affected. Surveys that draw data from general practice, as well as oncology and dental specialties, contribute to a broader understanding of how Prolia interacts with oral health.
Background and Context
Historical Background
The awareness of ONJ as a side effect began surfacing years prior to the introduction of Prolia. Initially tied to bisphosphonates—another class of medications for osteoporosis—ONJ's link to various therapies has been recognized. As Prolia gained traction post-2010, original studies identified the drug's adverse effects on jaw health, requiring a narrative shift in how healthcare providers approached patient education and treatment plans.
Current Trends in the Field
A growing body of literature highlights ONJ risk amongst Prolia users, emphasizing the importance of multidisciplinary care. Healthcare professionals, particularly dentists and oncologists, are increasingly engaged in patient treatment protocols. Current guidelines promote early intervention, with screenings before and during Prolia therapy to detect signs of jaw complications.
In alignment with these developments, educational initiatives have surfaced to equip clinicians with the necessary tools and knowledge to navigate this nuanced terrain. As scientific inquiry continues, the goal remains to better inform strategies to mitigate ONJ risk while maximizing the benefits of Prolia for those battling osteoporosis.
Prolusion to Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) is an intricate and concerning condition that poses a unique challenge within the realm of dental and medical practice. As healthcare continues to evolve, more attention is being paid to ONJ—especially in light of the medications prescribed for osteoporosis, such as Prolia. Understanding ONJ is not just an academic pursuit; it has real implications for treatment outcomes and patient quality of life.
This article aims to shine a light on the importance of ONJ in the context of Prolia treatment, revealing critical insights into how disease processes, medical history, and patient factors intertwine. With ONJ potentially resulting in serious complications, researchers and clinicians alike are urged to delve deeper into its etiology and incidence rates.
Here are some significant elements worth considering:
- Prevalence and Clinical Relevance: ONJ does not merely present as a statistical anomaly; it can drastically affect a patient's ability to perform daily tasks, including eating and speaking. Understanding its incidence is critical for improving patient outcomes.
- Connection with Medications: Medications like Prolia, which target bone density, have been linked to ONJ. Knowledge of this connection is essential for practitioners prescribing such drugs, especially as they weigh the benefits against potential risks.
- Preventive Measures: Awareness of ONJ facilitates early intervention strategies that can potentially mitigate the occurrence of this condition. Developing guidelines and recommendations based on the latest research can equip healthcare professionals with tools to manage at-risk patients effectively.
To grasp the full scope of ONJ, it is essential to start by defining this condition clearly. Not only does this provide a foundation for further discussion, but it also sets the stage for understanding related historical trends and medical practices.
Defining Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
Osteonecrosis of the jaw refers to a severe bone disease characterized by the death of bone tissue in the jaw area due to insufficient blood supply, trauma, or, as is often the case, certain medications. People affected by ONJ might experience pain, swelling, and exposed bone, leading to an array of distressing symptoms that can impair their quality of life.
While the condition can occur spontaneously, it often correlates with the use of bisphosphonates and denosumab, key players in the management of bone diseases. In particular, Prolia, which contains the active substance denosumab, has drawn scrutiny due to its possible link with the development of ONJ. Clinical reports suggest that prolonged exposure to these medications leads to significant suppression of bone remodeling processes, thereby increasing the risk of necrosis.
An essential takeaway here is that early diagnosis and intervention are paramount. Recognizing the signs of ONJ can enable healthcare providers to initiate appropriate treatment plans and encourage regular monitoring of at-risk individuals.
Historical Context
The understanding of osteonecrosis has evolved significantly over the years. Originally, the concept of necrosis was broadly applied across various body parts, but it wasn't until the late 20th century that specific focus was directed towards osteonecrosis, particularly regarding the jaw.
Historical cases noted that individuals undergoing treatment for cancer with bisphosphonates began reporting jaw-related complications. However, it wasn't until around the mid-2000s that the connection between these medications and ONJ became widely recognized within scientific literature. Clinical studies rapidly emerged, attempting to unscramble the why and how of this unforeseen complication.
As healthcare professionals began to compile data, they could outline several key factors:
- Patient Demographics: Early observations showed that ONJ was more prevalent in certain populations, notably those with pre-existing dental issues or undergoing invasive dental procedures.
- Mechanistic Insights: Researchers began to delve into the biological mechanisms, noting how the inhibition of RANKL—and thus, osteoclast activity—could lead to impaired bone maintenance and ultimately necrosis.
Through continuous research and advocacy, awareness grew, paving the way for modern clinical practice and guidelines. Now, understanding the historical trajectory of ONJ informs better treatment approaches and patient management strategies. The work remains ongoing as the medical community seeks to minimize risks while maximizing benefits for patients using treatments like Prolia.
Understanding Prolia and Its Usage
Understanding Prolia is crucial for those studying osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) as it directly ties into the broader discussion of treatment efficacy and safety. Prolia, a brand name for denosumab, is primarily used in managing osteoporosis. For patients at risk of fractures due to weakened bone structure, Prolia offers a mechanism that helps lower the risk of significant bone loss. The goal of this section is to unpack how Prolia functions and under what circumstances it is prescribed, presenting both its benefits and potential drawbacks.
Mechanism of Action
Prolia works by inhibiting a protein called RANKL. This protein is essential for the formation, function, and survival of osteoclasts—cells that break down bone. You can think of RANKL as a sort of "traffic cop" signaling the osteoclasts to do their job. By blocking RANKL, Prolia effectively reduces osteoclast activity, leading to a decrease in bone resorption. This process allows for enhanced bone density over time.
Here’s how the mechanism unfolds in simpler terms:
- Blockade of RANKL: Prolia binds to RANKL, preventing it from interacting with its receptor on the osteoclasts.
- Reduction in Bone Resorption: With fewer functioning osteoclasts, there’s a reduction in the breakdown of bone.
- Increase in Bone Density: Over time, this leads to an increase in bone mass, which is beneficial for osteoporosis patients.
This targeted action underscores why Prolia has gained traction in treating those with significant bone health issues. However, the inhibition of bone remodeling also raises concerns, particularly regarding ONJ.


Indications for Treatment
Prolia is indicated for populations with specific health challenges. These include:
- Postmenopausal Women: Particularly those at an elevated risk of osteoporosis-related fractures.
- Men with Osteoporosis: Especially those who have a history of fractures or similar risks.
- Patients on Glucocorticoids: Long-term steroid users often experience bone loss and can benefit from Prolia's protective effects.
- Bone Health in Cancer Patients: Some patients undergoing cancer treatment that affects bone density may also be good candidates for Prolia.
Despite Prolia's benefits, it’s essential to weigh the advantages against the potential risks. Osteonecrosis of the jaw is a serious consideration for any clinician prescribing this treatment, especially if a patient has existing dental issues or undergoes invasive dental procedures. Hence, understanding both the mechanism and indications is vital to ensure informed decision-making in treatment planning.
Incidence Rates of Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
Understanding the incidence rates of osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) is crucial for both patients and healthcare providers, especially in the context of treatments like Prolia. By analyzing how often ONJ occurs among those receiving this medication, healthcare professionals can better gauge the potential risks and facilitate informed decisions about treatment plans. This investigation is not merely academic; it holds substantial implications for patient management, influencing preventive strategies and emphasizing the need for vigilant monitoring.
Review of Current Data
Current research provides a spectrum of data on the incidence of ONJ in patients treated with Prolia. Reports suggest that the rates vary, with some studies indicating an incidence as low as 0.3%, while others document rates significantly higher in certain populations. Factors contributing to this variation include patient demographics, concurrent medications, and underlying medical conditions.
Moreover, data from clinical trials and post-marketing surveillance have revealed that individuals with a history of dental procedures or those with pre-existing dental health issues may be at elevated risk for developing ONJ. For instance, a recent cohort study noted that patients who underwent tooth extractions presented a higher incidence of ONJ post-treatment with Prolia compared to those who did not. These findings highlight how pre-treatment dental conditions can interplay with medication effects.
"The relationship between dental health and medication like Prolia needs to be underscored in patient education to mitigate risks effectively."
Comparative Studies with Other Medications
When comparing the incidence of ONJ related to Prolia with other osteoporosis treatment options, such as bisphosphonates, the differences become apparent. Bisphosphonates are often associated with higher incidences of ONJ, with some data suggesting rates around 1% to 10%, depending on the duration of therapy and additional risk factors. In contrast, the incidence rates surrounding Prolia might appear more favorable, but this should not lead to complacency.
In one comparative analysis, researchers explored ONJ occurrences in patients on Prolia versus those on bisphosphonates. They found that while Prolia presented a lower incidence overall, specific subgroups, particularly those with additional risk factors like cancer or high-dose corticosteroids, displayed incidence rates similar to those on bisphosphonates. This raises important considerations for patient assessment and the need for personalized treatment approaches. The nuanced understanding of the risks associated with these medications reinforces the importance of thorough patient evaluations and risk management strategies.
As healthcare bears the weight of these insights, the fact remains that patient education must be robust, urging individuals to maintain dental hygiene and regularly consult their dental practitioners. This collaboration is paramount; after all, leveraging insights from ongoing studies and patient experiences will pave the way for better clinical outcomes in the future.
Pathophysiology of Osteonecrosis in Prolia Users
Understanding the pathophysiology behind osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) in patients treated with Prolia is crucial for recognizing the risks associated with this medication. With Prolia, which is primarily designed to manage osteoporosis, there's a delicate balance between preventing fractures and ensuring bone health without fostering the conditions that could lead to ONJ.
Bone Remodeling Processes
Bone is a dynamic organ, constantly undergoing remodeling through the intricate processes of bone resorption and formation. In healthy individuals, bone tissues are continuously broken down by cells known as osteoclasts and subsequently rebuilt by osteoblasts. This cycle is essential for maintaining bone density and strength.
- In patients taking Prolia, the drug inhibits a crucial protein called RANKL, which is necessary for the formation and activity of osteoclasts.
- This inhibition means that bone resorption is significantly reduced. While this might sound beneficial at first glance, it can lead to an accumulation of dead bone cells. These cells create a conducive environment for ONJ, particularly when there is a disruption in the normal healing processes after dental procedures or oral traumas.
The interruption of natural bone turnover can, therefore, cause a backlog of microinjuries not efficiently repaired. As osteoclast activity wanes, the jawbone might develop necrotic areas, especially if other risk factors come into play, like local infections or poor dental hygiene. Ultimately, this could culminate in symptoms typical of ONJ, laying bare the paradox where a treatment meant to strengthen bones can inadvertently contribute to their decay in certain contexts.
Impact of RANKL Inhibition
The role of RANKL inhibition through Prolia is pivotal to the drug's effectiveness in managing osteoporosis. However, it has critical implications for jaw health as well.
Key Considerations:
- Reduced Bone Remodeling: While osteoclasts are harmful in certain arenas, their function is vital for remodeling bone to adapt to stress and heal injuries. With Prolia's inhibition of RANKL, this balance is skewed, creating a static bone environment that may resist healing.
- Increased Risk Factors: Patients on Prolia may be more sensitive to dental procedures, which could otherwise be routine. The risks of extraction, implants, or even just prolonged illness or poor oral hygiene may manifest as more severe complications.
- Compounding Conditions: If a patient has existing risk factors — such as being on bisphosphonates or having cancer diagnoses, for instance — the risk of developing ONJ escalates. RANKL's role in inhibiting RANKL doesn't disappear but shifts focus. Hence, when patients do not align their oral health with their treatment plan, the risk of osteonecrosis escalates.
Being aware of these factors allows for more informed decisions by healthcare providers and emphasizes the importance of dialogue between patients and professionals about the risks associated with treatment.
Risk Factors for ONJ in Patients Using Prolia
Understanding the risk factors associated with osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) in patients using Prolia is not just academically interesting; it holds significant clinical relevance. The connection between medication usage and the likelihood of complications, like ONJ, urges us to evaluate our patients comprehensively. Identifying specific risk factors can lead to improved patient management, tailored treatment strategies, and greater overall awareness. Knowing who is vulnerable allows healthcare providers to make sound, evidence-based decisions.
Demographic Variables
Demographic variables play a critical role in the incidence of ONJ among Prolia users. Age is a significant starting point. Older adults, particularly those over 65, often face higher incidence rates of bone issues and associated complications due to age-related physiological changes. This group typically has more comorbidities, which adds layers of complexity to their health profiles. Moreover, gender can also influence risk. Studies suggest that females may be more affected than males, potentially due to hormonal differences impacting bone remodeling.
In addition to age and gender, other factors like race or ethnicity can also potentially affect the incidence of ONJ. Research indicates that certain racial groups may possess genetic predispositions that alter bone density and health. While the data on demographics is evolving, it's clear that these variables should not be overlooked in your clinical assessments. Understanding these patterns can help guide treatment plans and preventative measures, as a one-size-fits-all approach often falls short in patient care.
Concurrent Medications and Conditions
When it comes to concurrent medications and underlying health conditions, the stakes get considerably higher for those undergoing Prolia treatment. Many patients take multiple medications to manage their health. Common culprits include bisphosphonates, corticosteroids, and certain anti-angiogenic agents, all known to affect jaw health negatively. When combined with Prolia, these medications can compound risks, increasing the likelihood of ONJ development.
It’s equally essential to consider systemic conditions present alongside osteoporosis. Patients with diabetes or inflammatory diseases such as rheumatoid arthritis often exhibit compromised healing processes, which complicates recovery from potential dental procedures or jaw issues. This raises another layer of caution among clinicians who treat patients on Prolia.
"The influence of concurrent health issues on healing and bone health emphasizes the need for multidisciplinary approaches in patient management."
Equipped with a solid understanding of risk factors—both demographic and pharmacological—healthcare providers can take proactive steps. Engaging in preventive measures, such as regular dental evaluations and patient education on oral hygiene, becomes critical. Knowing who is at higher risk helps to tailor monitoring and intervention strategies effectively, ensuring that the potential for ONJ is minimized in those on Prolia.
By addressing these specific elements, we pave the way for more informed, patient-centric discussions surrounding ONJ and Prolia treatment.
Symptoms and Diagnosis of Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
Osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) can pose serious challenges to both patients and healthcare providers, especially in the context of Prolia treatment. Early recognition of the signs and symptoms of ONJ is crucial for timely intervention. Understanding these clinical manifestations, as well as the diagnostic protocols available, ensures that providers can effectively manage the complications arising from this condition. This section delves into the various symptoms associated with ONJ and outlines the diagnostic techniques currently employed in medical practice.
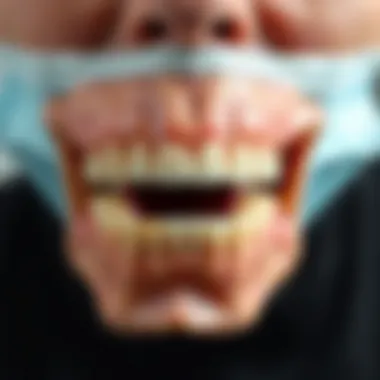

Clinical Manifestations
The clinical signs of osteonecrosis of the jaw often manifest subtly at first, which may lead to delays in diagnosis. Patients receiving Prolia may experience a range of symptoms, including:
- Localized Pain: Often, patients report a pain that seems concentrated in the jaw or around the teeth. This discomfort can be dull or sharp, making it hard for patients to pinpoint its origin.
- Swelling: Inflammation in the jaw area can be a tell-tale sign. Swelling may occur in the gums or the jaw itself, potentially indicating underlying issues.
- Exposed Bone: Perhaps the most distinct sign, the visibility of necrotic bone can be alarming. This occurs when the blood supply to the jawbone diminishes, leading to its degradation.
- Altered Sensation: Patients may report numbness or a tingling sensation in the affected area. This can contribute to a significant decline in quality of life.
- Infection: On occasion, secondary infections can develop, characterized by pus formation and increased pain. Patients might notice bad breath or a foul taste if such infections arise.
These symptoms can easily be misattributed to dental problems or other conditions, which complicates the clinical picture.
Diagnostic Techniques
Diagnosing ONJ requires a multifaceted approach to accurately identify the extent of the disease. Several techniques are employed:
- Clinical Examination: A thorough physical exam is crucial. Dentists and physicians often look for the classic signs of ONJ, such as exposed bone or signs of infection.
- Imaging Studies: Radiographic examinations, particularly X-rays, provide valuable insights into the bone integrity within the jaw. Advanced modalities like CBCT (Cone Beam Computed Tomography) may also be used for a three-dimensional view, helping to assess bone quality and structure.
- Biopsy: In unclear cases, a biopsy may be performed. This involves taking a small sample of bone tissue to analyze it for necrotic changes or signs of infection.
- Blood Tests: Assessing for related conditions, such as infection or systemic diseases, can contribute to understanding the broader aspects of a patient's health that may be affecting jaw health.
Early detection and diagnosis are key in managing osteonecrosis of the jaw. By employing comprehensive clinical assessments and advanced imaging techniques, healthcare professionals can devise effective treatment plans tailored to individual patient needs.
In summary, heightened awareness of the symptoms and a diverse range of diagnostic tools are essential for effective management of ONJ in patients undergoing Prolia treatment. Recognizing these elements can significantly influence the outcomes of affected individuals.
Preventative Strategies for ONJ
The management of osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) is increasingly significant in the context of Prolia treatment, primarily because of the drug's impact on bone metabolism. Defining clear preventative strategies becomes pivotal for both patients and healthcare providers. These strategies are essential not just for minimizing the risk of ONJ but also for fostering a comprehensive approach to patient care. Effective preventative measures can significantly improve outcomes, enhance quality of life, and reduce the need for more invasive interventions later on.
Oral Health Recommendations
Maintaining oral health is a cornerstone in preventing ONJ. It's critical that patients on Prolia follow rigorous dental care practices. Here are some key recommendations:
- Regular Dental Check-ups: Patients should see a dentist at least every six months to monitor oral health and catch any potential issues early.
- Daily Oral Hygiene: Brushing twice a day and flossing regularly can help keep bacteria at bay. Using an antiseptic mouthwash may also reduce the risk of infections.
- Dietary Considerations: A nutrient-rich diet supports bone health. Staying hydrated and limiting sugary or acidic foods may also contribute to better oral health.
- Avoiding Tobacco and Alcohol: Both tobacco use and excessive alcohol consumption are detrimental to bone health and can exacerbate the risk of developing ONJ.
- Addressing Dental Procedures: If surgical procedures like tooth extractions or implants are needed, patients should consult their healthcare team for specific precautions and timing in relation to Prolia injections.
These recommendations not only target dental health but create a broader culture of wellness that emphasizes the preventive aspects of care.
Patient Education
Educating patients is crucial for effective preventive strategies against ONJ. Knowledge empowers patients to participate actively in their care, which in turn can lead to better health outcomes. Here are several points that should be addressed during patient education sessions:
- Understanding ONJ: Patients need to know what osteonecrosis of the jaw is, its symptoms, and its potential relationship with Prolia. This basic understanding can encourage vigilance regarding oral health.
- Awareness of Risk Factors: Patients should be informed about the various risk factors associated with ONJ, such as concurrent medications, pre-existing dental issues, and overall health conditions.
- Medication Compliance: It's critical that patients understand the importance of taking Prolia as prescribed. Skipping doses not only reduces the medication’s effectiveness but may also contribute to complications, including ONJ.
- Engagement in Dialogue: Encourage patients to discuss their concerns and experiences openly with both their dentists and healthcare providers. This ongoing conversation can lead to individualized approaches to care that address unique risks.
- Resources and Support: Provide patients with access to educational materials, support groups, or online resources, such as those found on NIDCR or Mayo Clinic.
In this context, effective communication regarding the risks and preventative strategies can lead to more proactive management of oral health and a reduced incidence of ONJ among patients using Prolia.
Management of Osteonecrosis of the Jaw
Understanding how to manage osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) in patients receiving Prolia treatment is crucial. The management process must be methodical, recognizing that proactive measures can significantly alter patient outcomes. Osteonecrosis of the jaw presents a unique set of challenges, particularly in patients who are already vulnerable due to underlying conditions like osteoporosis. Thus, effective management encompasses not only treatment but also prevention and patient education.
The significance of thorough management strategies cannot be overstated. Early intervention can minimize the risks associated with ONJ and lead to better recovery experiences for patients. This includes a range of approaches tailored to each individual's medical and dental background. By integrating best practices in patient management, healthcare providers can help mitigate the incidence of ONJ and offer more comprehensive care.
Treatment Approaches
The treatment approaches for ONJ are varied and depend largely on the stage of the disease and the severity of symptoms. If a patient presents with early signs of ONJ, conservative management may include:
- Antibiotic therapy: Used to manage infections and promote healing.
- Oral rinses: Antiseptic mouthwashes can reduce bacterial load and help maintain oral hygiene.
- Chlorhexidine mouthwash: Commonly recommended for its antimicrobial properties.
In more advanced cases where such approaches fail, it becomes necessary to explore more aggressive interventions. Medications like bisphosphonates may need to be reassessed, and, in some circumstances, adjustments to existing medications may be called for to alleviate symptoms and promote healing.
One promising aspect of treatment is the potential role of growth factors and regenerative medicine. Studies have suggested that these could help in the healing process of bone tissue. Further research is needed, but they hold the promise of advancing treatment options beyond traditional methods.
Surgical Interventions
When conservative treatments don’t provide relief or if the ONJ progresses, surgical interventions become necessary. Surgical management of ONJ can include:
- Bone debridement: This involves the surgical removal of necrotic bone to reduce pain and infection, promoting healing in the surrounding healthy tissue.
- Osteotomy: In severe cases, reconstructive surgery may be needed, which can involve the removal of significant portions of the jaw. This can be challenging and requires skilled surgical intervention.
The decision to pursue surgery is not taken lightly. It requires careful consideration of the patient's overall health, the extent of the ONJ, and the potential risks involved with the procedure. This is where healthcare providers, along with dental professionals, must work closely together to formulate a comprehensive surgical plan.
A multidisciplinary approach improves the accuracy of diagnosis and treatment planning, ensuring that patients achieve optimal outcomes after surgical interventions.
It's worth noting that surgical intervention carries its risks, particularly in patients who are already compromised due to osteoporosis and bone density issues. Therefore, patient counseling and shared decision-making are vital aspects of this management phase, informing the patient about both benefits and potential complications.
Long-Term Outlook for Patients
The long-term outlook for individuals receiving Prolia treatment is a pivotal focus when discussing the incidence of osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ). This section aims to illuminate the consequences that prolonged use of Prolia could have on jaw health, affecting not just bone density but also the overall quality of life. One of the first elements to consider is the proactive management of potential complications arising from ONJ—being mindful of risks can greatly influence patient care strategies and outcomes.
Prognosis of ONJ
Understanding the prognosis of ONJ in the context of Prolia treatment is crucial for both healthcare providers and patients. The long-term risks associated with this medication, particularly given its influence on bone remodeling, necessitate thorough evaluations. Recent studies suggest that while many patients experience improved bone density and a reduction in fracture risk, the potential onset of ONJ cannot be ignored.
Factors that might affect the prognosis include:


- Early Detection: Identifying symptoms like jaw pain or swelling at the outset can facilitate timely intervention.
- Patient Demographics: Age, underlying health conditions, and other medications can dramatically change outcomes.
- Adherence to Oral Health Guidelines: Regular dental check-ups and maintaining excellent oral hygiene are instrumental in mitigating risks.
Statistically, the occurrence rate of ONJ varies, with reports indicating incidences ranging from 0.5% to 1% among patients treated with Prolia. These numbers highlight the significance of patient education and informed consent about the risks involved.
Considerations for Future Treatments
As the field advances, new treatments and methodologies are continually researched to address the complications associated with Prolia. Looking ahead, several considerations warrant attention:
- Innovative Medication Alternatives: Understanding alternatives that may present fewer risks for developing ONJ is essential. Research is underway focusing on drugs that target similar pathways but with a different safety profile.
- Enhanced Monitoring Protocols: Future strategies may emphasize improved monitoring using advanced imaging techniques for early diagnosis of ONJ. This could lead to better preventative measures tailored specifically to those on prolonged treatment regimes.
- Clinical Guidelines Revision: As more data emerges, ongoing assessments of clinical guidelines will be necessary. Engaging with dental professionals earlier in the treatment process can help align both medical and dental care efforts.
In closing, while Prolia presents definitive benefits for patients with osteoporosis, the long-term implications regarding ONJ cannot be overlooked. Awareness, vigilance, and a collaborative approach to patient care are essential to navigating this complex landscape effectively.
"Failing to prepare is preparing to fail." - John Wooden
Understanding the long-term outlook for patients receiving Prolia not only shapes treatment protocols but also fosters better patient-provider dialogues, enhancing the overall treatment experience.
Implications for Healthcare Providers
The implications for healthcare providers regarding the incidence of osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) associated with Prolia treatment are substantial. Given the increasing use of direct-acting medications like Prolia, understanding the potential risks becomes imperative for those managing patient care. This section will explore critical elements such as patient monitoring, interdisciplinary collaboration, and educational requirements for ensuring optimal outcomes.
Monitoring Patients on Prolia
Monitoring patients on Prolia involves a multi-faceted approach that encompasses regular assessments and vigilance for early signs of ONJ. As healthcare professionals, keeping a keen eye on oral health is as crucial as the effects of the medication itself. Patients should be encouraged to communicate any dental pain, lesions, or infections at the onset. To streamline this process:
- Initial Assessment: Conduct thorough dental evaluations before starting treatment with Prolia to establish baseline oral health status.
- Regular Follow-ups: Schedule follow-up visits every six months to monitor dental health. This practice helps in identifying potential complications at an early stage.
- Patient Education: Provide clear guidance for patients about the signs and symptoms of ONJ. The more informed they are, the faster they can seek help if needed.
"Vigilance in monitoring can help catch any adverse reactions early, making all the difference in patient outcomes."
Engaging patients in self-monitoring can also be beneficial. Encourage them to maintain oral hygiene and seek dental care proactively. This two-way communication can lead to better management and a clearer understanding of the relationship between Prolia and ONJ.
Collaboration with Dental Professionals
Collaboration with dental professionals plays a pivotal role in mitigating the risks associated with Prolia. The intersection of dental and medical fields is crucial, as dental health can directly influence the effectiveness and safety of osteoporosis treatments. To foster better collaboration:
- Interdisciplinary Meetings: Organize regular meetings between dental and medical teams to discuss treatment plans and any complications regarding patients being treated with Prolia.
- Referral Policies: Establish clear referral guidelines for patients who exhibit signs of ONJ. This helps ensure they receive timely dental care from specialists well-versed in ONJ management.
- Shared Resources: Utilize resources from both the medical and dental perspectives, incorporating protocols from dental professionals into overall patient treatment strategies.
Ultimately, aligning strategies between healthcare providers and dental professionals can help create a seamless care experience for patients. Overall, these collaborative efforts underscore the concept that effective healthcare delivery requires a multidisciplinary approach in cases involving potent medications like Prolia.
Summary of Key Findings
The connection between Prolia treatment and osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) is crucial for understanding the broader implications of this medication. Prolia, also known by its generic name denosumab, is frequently prescribed to prevent fractures in individuals with osteoporosis. However, the possibility of developing ONJ while on this treatment has raised significant concerns among healthcare providers and patients alike.
Recap of ONJ Incidence
Recent studies indicate that the incidence of ONJ in patients treated with Prolia varies, but it is generally perceived as an uncommon complication. Research shows that the rates of ONJ in these patients can range from about 0.5% to 5%. Factors that seem to influence the prevalence include age, type of underlying disease, and any concomitant therapies, particularly corticosteroids or chemotherapy.
Interestingly, some reports suggest that the incidence could be higher when compared to patients using bisphosphonates, although the absolute risk remains relatively low. Notably, patients with a history of dental issues or those who have undergone dental procedures while receiving Prolia therapy appear to be at an increased risk for developing ONJ.
Understanding the nuances of these incidence rates is essential for healthcare practitioners to better monitor and manage the risks associated with Prolia treatment and to conduct preemptive strategies aimed at reducing the likelihood of ONJ.
Final Thoughts on Prolia
Overall, the landscape of treating osteoporosis with Prolia presents a double-edged sword. On one hand, the medication effectively reduces fracture risk and is a pivotal therapy for many patients. On the other hand, there’s the potential for serious side effects like osteonecrosis of the jaw, which demands vigilant observation.
Healthcare providers must weigh the benefits against the risks carefully. Emphasis must be placed on patient education regarding oral hygiene and the importance of dental check-ups during treatment. Additionally, it’s imperative for ongoing research to continue further dissection of the relationship between Prolia and ONJ. Any findings will contribute to refining treatment strategies and improving patient outcomes.
"Understanding the delicate balance between therapeutic benefits and potential risks can empower patients and providers alike to make informed decisions." - A seasoned researcher in osteoporosis treatment.
Future Directions in Research
As the medical community continues to grapple with the complexities of osteonecrosis of the jaw (ONJ) associated with Prolia treatment, the need for further inquiry into this serious issue becomes apparent. Researchers are not only looking into understanding the underlying mechanisms of ONJ but are also exploring ways to mitigate its risks during Prolia therapy. This section will delve into emerging studies and innovative treatment protocols, giving a comprehensive view of forthcoming research in this crucial field.
Emerging Studies on ONJ
Recent efforts have highlighted an increased interest in the incidence rates of ONJ among patients on Prolia. New studies aim to quantify these rates more accurately, taking into consideration various risk factors such as duration of therapy, underlying health conditions, and concurrent medications. Some noteworthy research initiatives include:
- Multicenter Collaborations: Institutions are pooling data to establish a broader understanding of ONJ. By collaborating across various healthcare settings, researchers can gather more extensive datasets that might reveal trends previously invisible in smaller studies.
- Longitudinal Observations: Extended studies are being designed to observe patients over time. The goal is to track the development of ONJ throughout the patients’ treatment journey, thereby identifying potential predictors of this condition.
- Patient-Centric Studies: New studies are emphasizing the patient experience. Surveys and interviews are being used to gather qualitative data on symptoms and treatment outcomes that purely clinical studies might overlook.
The importance of these studies cannot be overstated, as they will aid in forming a more nuanced understanding of ONJ and facilitate the development of targeted preventative measures.
Innovations in Treatment Protocols
In the face of rising concerns surrounding ONJ associated with Prolia, healthcare professionals are keenly interested in innovative treatment protocols. Here are some areas currently being explored:
- Personalized Treatment Plans: By analyzing the genetic makeup and overall health of patients, treatments can be tailored specifically to individual needs. This ensures a more proactive approach rather than a reactive one, potentially reducing incidents of ONJ.
- Pharmaceutical Alternatives: Research is ongoing into alternative medications for osteoporosis that might pose less risk in terms of ONJ. Identifying drugs with similar efficacy but a more favorable safety profile is essential for patient safety.
- Nutritional Interventions: Some studies are investigating whether dietary changes or supplements can play a role in bone health during Prolia treatment. Nutrients like calcium and vitamin D are essential, but precise dietary adjustments may also enhance the resilience of bone tissue.
**"As we venture into the unknown, the goal remains clear: safeguard health while maximizing therapeutic benefit."
Overall, the future of ONJ research and treatment associated with Prolia is filled with promise. The landscape is shifting as researchers and clinicians come together to tackle the challenges posed by ONJ, working towards innovative strategies that can enhance patient outcomes.
By focusing on both emerging studies and innovative treatment protocols, the medical community can hope to minimize the impacts of ONJ while still providing effective care for osteoporosis patients.







