Understanding the Pelvis Bone in Women: Structure and Function

Intro
The pelvis bone plays a crucial role in a woman's anatomy and functions. Understanding its structure and significance is essential for recognizing its implications on health throughout various life stages. The pelvis acts not only as a support structure for the body but also has essential roles in reproductive health and movement.
Research Overview
Key Findings
Research indicates that the pelvic structure varies significantly among women. Factors such as genetics, hormonal changes, and physical health influence its shape and function. The pelvis supports the weight of the upper body, facilitates movement, and is crucial during childbirth. A well-functioning pelvis contributes to overall health, while disorders can affect mobility and reproductive capabilities.
Study Methodology
To gather insights on the pelvis bone, studies often employ a range of methodologies. Some use imaging techniques such as MRI or CT scans to visualize pelvic anatomy in three dimensions. Others utilize surveys and clinical evaluations to assess the functional aspects of the pelvis in different populations. Data from these studies often highlight the importance of understanding both the normal variations and pathological conditions associated with the pelvis.
Background and Context
Historical Background
The examination of pelvic anatomy dates back to ancient civilizations. Over centuries, medical knowledge regarding the pelvis has evolved significantly. Historical texts often focused on its role in childbirth, but modern studies broaden this perspective, recognizing its multifaceted functions.
Current Trends in the Field
Today, there is a growing emphasis on integrative approaches that encompass anatomy, physiology, and clinical practices related to the pelvis. Research now includes the impact of lifestyle choices and environmental factors on pelvic health. Orthopedic studies also highlight conditions like pelvic floor disorders, which have gained attention for their prevalence and impact on women's quality of life.
Understanding the pelvis is vital for addressing health issues that affect women's overall well-being. It is not just an anatomical structure, but a key player in functional and reproductive health.
Increasing awareness around these topics is crucial, especially among healthcare professionals, educators, and researchers. This deep dive into the pelvis enhances insights into its complexities and helps improve therapeutic approaches.
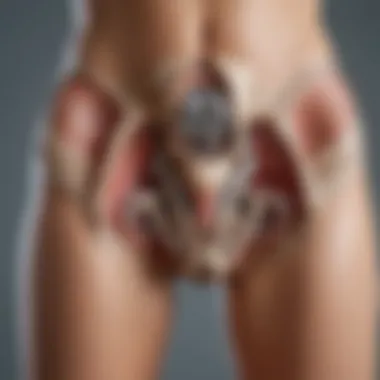
Anatomy of the Pelvis Bone
Understanding the anatomy of the pelvis bone is crucial because it lays a foundation for comprehending its various functions and implications in women’s health. The pelvis is not just a bony structure; it is a complex combination of bones, ligaments, and muscles that work synergistically. Knowledge of the pelvic anatomy is essential for healthcare professionals, especially for those working in gynecology, obstetrics, and physiotherapy. It has implications for clinical practices, surgical interventions, and understanding conditions that can affect pelvic health. Hence, an in-depth exploration of the pelvic anatomy helps in grasping its broader importance.
Overview of Pelvic Structure
The pelvis is a basin-shaped structure that connects the trunk to the lower limbs. It supports the weight of the upper body when sitting or standing and plays a significant role in locomotion. Structurally, the pelvis consists of several bones that form both the pelvic cavity and the pelvic girdle. The unique form of the pelvis is what differentiates it in males and females, primarily due to the needs of childbirth in females. This adaptation makes understanding the pelvic structure more significant for women.
Components of the Pelvis
The pelvis is comprised of several key components, each playing a specific role:
Ilium
The ilium represents the largest part of the pelvis. Its shape resembles a broad, fan-like structure and contributes significantly to the pelvic region's stability. Its unique characteristic is the iliac crest, which is a prominent ridge that is palpable and serves as an attachment point for various muscles. The iliac broadly supports the pelvic organs and assists in load transfer to the legs. However, the ilium can also be susceptible to injuries, especially during high-impact activities.
Ischium
The ischium is the lower and back part of the pelvis. One key aspect of the ischium is the ischial tuberosity, often referred to as the 'sit bones.' This area provides important support during sitting, bearing the body’s weight. A unique feature of the ischium is its role in the formation of the pelvic floor, thus impacting overall pelvic health. It can sometimes be an area of soreness for individuals who spend long periods seated.
Pubis
The pubis is the front portion of the pelvis. Its most notable aspect is the pubic symphysis, a fibrocartilaginous joint that allows for slight movement, which is particularly important during childbirth. This adaptability makes the pubis critical for reproductive health. The pubis can also be a site of discomfort in cases of pelvic joint dysfunction, highlighting its clinical relevance.
Sacrum
The sacrum is a large, triangular bone located at the base of the spine. It is the keystone of the pelvis, forming the posterior wall. One key characteristic of the sacrum is its fusion of five vertebrae, which provides strength and stability to the pelvic region. Its unique disposition allows for load-bearing and mobility. Nevertheless, the sacrum can be prone to degeneration with age, influencing overall pelvic stability.
Coccyx
The coccyx, or tailbone, is a small, triangular bone at the bottom of the sacrum. It plays a significant role in supporting the pelvic organs and contributes to pelvic floor strength. The coccyx has a unique characteristic in that it can be a source of pain, commonly referred to as coccydynia. Understanding its role can be crucial when addressing pelvic floor disorders, often found in women.
Pelvic Dimensions
The dimensions of the pelvis are vital for both functional and clinical reasons. They are considered during childbirth and have implications for various medical conditions.
Pelvic Inlet
The pelvic inlet is the upper opening of the pelvic cavity. Its shape and size are significant in determining the feasibility of vaginal delivery. The key characteristic of the pelvic inlet is its importance in defining the anatomical orientation between the true pelvis and the false pelvis. A broader pelvic inlet can facilitate childbirth, while a narrower inlet may complicate labor.
Pelvic Outlet
The pelvic outlet refers to the lower opening of the pelvic cavity. One important aspect of the pelvic outlet is its role in childbirth, as it is the passage through which the baby exits the birth canal. This outlet's unique feature lies in its variability, which can affect the ease of labor. Assessing the pelvic outlet dimensions can be crucial for healthcare providers when planning delivery.
Pelvic Cavity


The pelvic cavity is the space enclosed by the pelvic bones. Its dimensions, shape, and depth are crucial for accommodating pelvic organs. The pelvic cavity's unique feature lies in its complexity, as it houses vital organs such as the bladder, uterus, and rectum. Knowledge about its dimensions is relevant for surgical procedures and understanding anatomical anomalies.
Functional Aspects of the Pelvis in Women
The study of functional aspects of the pelvis in women is crucial for comprehending its various roles in health and biomechanical activities. The pelvis is not just a bone structure; it contributes significantly to mobility, childbirth, and stability. As this article unfolds, it is vital to connect these functional aspects to their practical implications. Understanding this helps researchers and practitioners devise strategies for improved health outcomes.
Role in Locomotion
The pelvis acts as a foundation that supports the spine and provides a stable base for the legs during movement. Its structure enables efficient transfer of weight and forces from the upper body to the lower limbs. The hip joints, which are integral components of the pelvis, allow for a wide range of motion. This mobility facilitates various activities, from walking to running. Any dysfunction in the pelvis can hinder locomotion, leading to discomfort, imbalance, or injury. Therefore, analyzing how the pelvis enables movement is fundamental to personal training and rehabilitation strategies.
Importance in Childbirth
The significance of the pelvis is underscored during childbirth. It serves as the birth canal through which a baby emerges. The complex anatomy of the pelvic structure supports this process while accommodating the demands placed on it during labor.
Pelvic Floor Support
Pelvic floor support plays a vital role in childbirth and throughout a woman's life. This support system is made of muscles and connective tissues, which help hold the pelvic organs in place. Strong pelvic floor muscles contribute to a smooth childbirth experience by supporting the uterus, bladder, and intestines. They also play a role in preventing pelvic floor disorders.
A key characteristic of pelvic floor support is its ability to react and adapt during labor, aiding in the delivery process. This dynamic capability makes it a crucial element in childbirth, empowering health professionals to apply targeted exercises for pregnant women to enhance their muscle strength. However, weakened pelvic floor muscles can lead to complications like incontinence or prolapse later in life.
Birth Canal Dynamics
Birth canal dynamics refers to the changes in pelvic morphology during childbirth. The adaptability of the pelvis allows it to shift shape as the baby moves through the canal. This characteristic is important since it can facilitate the delivery process, sometimes making it smoother.
The unique advantage of understanding birth canal dynamics lies in its potential to inform medical practices. For instance, healthcare providers can develop individualized childbirth plans based on a woman's pelvic structure. Conversely, changes that hinder these dynamics can contribute to complications, emphasizing the need for monitoring during pregnancy.
Impacts on Posture
The pelvis is central to human posture. It connects the upper body with the lower limbs, influencing how we stand, walk, and sit. A well-aligned pelvis allows for correct spinal positioning, which is essential for maintaining overall health.
Postural imbalances often stem from pelvic misalignments. These can result in pain and discomfort in other areas, notably the back and hips. Understanding the relationship between the pelvis and posture can lead to preventive measures and treatments aimed at correcting these issues.
Hormonal Influence on Pelvic Anatomy
Hormones play a critical role in shaping the pelvic anatomy in women. These biochemical messengers influence development, function, and overall well-being. The importance of understanding how hormones like estrogen and progesterone affect the pelvic region cannot be overstated, especially considering their implications on health and reproduction. By examining these hormonal influences, we can gain insights into the complexity of pelvic anatomy and its relevance throughout a woman's life.
Effects of Estrogen
Estrogen is a key hormone impacting the pelvic anatomy. It is primarily produced in the ovaries and is crucial during various life stages. This hormone affects the growth and maintenance of pelvic structures. One major effect of estrogen is the promotion of bone density. This is particularly important for the pelvis, as it is essential for supporting the weight of the upper body and maintaining stability during movement.
- Bone Development: Increased estrogen levels lead to enhanced bone growth and density, vital for maintaining optimal pelvic structure.
- Soft Tissue Changes: Estrogen also influences the ligaments and muscles surrounding the pelvis. It helps in maintaining flexibility and strength, which can impact physical activities.
- Menstrual and Reproductive Health: Estrogen regulates the menstrual cycle, affecting not just the ovary function but also the pelvic floor's response during reproductive processes.
"Understanding estrogen's role in pelvic health can illuminate many conditions faced by women, ranging from osteoporosis to menstrual disorders."
Impact of Progesterone
Progesterone, another key hormone, has distinct effects on the pelvic anatomy. It is primarily produced after ovulation and plays a crucial role in regulating menstrual cycles and supporting pregnancy.
- Muscle Relaxation: Progesterone induces relaxation in pelvic muscles. During pregnancy, this is essential as it allows the pelvis to expand for childbirth, altering its anatomical structure to accommodate the growing fetus.
- Increased Blood Flow: Progesterone enhances blood flow to the pelvic region, which can impact inflammation and repair processes.
- Role in Pregnancy: Its effects during pregnancy are profound, influencing everything from the labor process to recovery postpartum.
Understanding the roles of estrogen and progesterone is vital, especially for clinicians dealing with women's health issues. There are implications such as hormonal therapies that could address pelvic-related symptoms or conditions.
The pelvic anatomy is not static but continually shaped by these hormonal influences. An awareness of how these hormones work can assist in better insights into treating various conditions related to women's health.
Pelvic Health and Women’s Health Issues
Pelvic health plays a critical role in the quality of life for women. This section delves into various health issues that affect the pelvis. Understanding these issues is essential, as they can significantly impact overall health, including reproductive function and physical well-being. Here, we explore pelvic floor disorders, menstrual health, and pregnancy-related concerns. Each topic contributes uniquely to the broader context of women's health, emphasizing the importance of proper pelvic health.
Pelvic Floor Disorders
Pelvic floor disorders are common but often underreported issues that affect many women. The pelvic floor supports the organs in the pelvis and its dysfunction can lead to various health problems.
Incontinence
Incontinence refers to the involuntary loss of urine. Many women experience this condition at some stage in their lives, especially after childbirth or with aging. It can lead to social discomfort and affect daily activities.
Key characteristics of incontinence include urgency and frequency of urination. Its prevalence makes it a significant aspect of pelvic health discussions. The condition does not only impact physical health but can also have psychological effects, making it a crucial topic in this article.
One unique feature of incontinence is its varied types, including stress and urge incontinence. Treatments such as pelvic floor exercises, medications, or surgery exist, but their effectiveness can vary among individuals. Understanding these treatments helps women access the appropriate management of this condition.
Prolapse
Prolapse occurs when pelvic organs like the bladder or uterus descend due to weakening of the pelvic floor muscles. This condition can lead to discomfort and complications, such as urinary difficulties.
The key characteristic of prolapse is the sensation of heaviness or bulging in the pelvic area. Given its impact on body image and physical activity, this makes it a relevant focus in the sphere of women’s health. Prolapse may also result in complications during childbirth or affect sexual function.
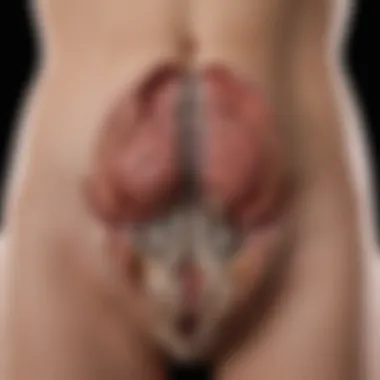

A unique feature of prolapse includes its classification into different types, such as uterine or cystocele prolapse. Treatment options are available, including lifestyle modifications, pelvic floor therapies, or surgical interventions. Being informed about these options assists women in choosing the best path for their health.
Menstrual Health
Menstrual health is another vital aspect of pelvic health. Menstrual cycles can vary widely among women, affecting physical and emotional well-being. Regular menstrual cycles are often a sign of good reproductive health, while irregularities can indicate underlying issues.
Awareness around menstrual hygiene is crucial. Women should practice health education to manage their cycles better and recognize signs of abnormalities, like severe pain or bleeding. Understanding the significance of hormonal changes during the menstrual cycle helps women make informed health choices.
Pregnancy and Postpartum Considerations
Pregnancy and postpartum periods bring unique challenges concerning pelvic health. These stages demand physical adjustments that can strain the pelvic region and affect recovery.
Pelvic Pain
Pelvic pain during pregnancy is a common experience. It can stem from hormonal shifts and physical changes. Women may feel discomfort in the pelvis or lower abdomen due to the growing uterus and hormonal adaptations.
The key characteristic of pelvic pain is its variability; some women may experience mild discomfort, while others suffer significant pain. This aspect is crucial to discuss because it can hinder daily activities and affect mental health during this sensitive time. Options like physical therapy may offer some relief but must be closely monitored for safety.
Recovery
Recovery after childbirth is crucial for restoring pelvic health. Women's bodies undergo substantial changes during pregnancy, and understanding the recovery process is essential.
Key characteristics of recovery include physical therapy, emotional health, and gradual return to activity. Attention to these factors can result in enhanced quality of life. Women may experience lingering issues such as pelvic pain or weakness in the pelvic floor muscles, which need addressing to prevent long-term consequences. Emphasizing a sensible approach to recovery can lead to better health outcomes.
"Understanding pelvic health issues ensures that women maintain a better quality of life and make informed decisions about their bodies and health."
Orthopedic Considerations Relevant to the Pelvis
The pelvis plays a vital role in many bodily functions, and orthopedic considerations are significant in examining musculoskeletal health. Understanding the orthopedic relevance of the pelvis is crucial for several reasons. First, orthopedics addresses injuries that commonly affect this area. Second, conditions like osteoporosis can have profound implications on bone integrity. Addressing these issues leads to improved health outcomes and better management of pelvic conditions.
Common Injuries Related to the Pelvis
Injuries to the pelvis can occur due to trauma, overuse, or degenerative processes. Common injuries include:
- Fractures: Pelvic fractures are often caused by falls or high-impact activities. They can range from minor to severe, depending on the force of the impact.
- Muscle Strains: Strains in the pelvic region, particularly in the hip flexors or gluteal muscles, are frequent in athletes and individuals engaged in high levels of physical activity.
- Tendonitis: Inflammation of the tendons around the pelvis can lead to discomfort and restricted movement, often exacerbated by repetitive physical stresses.
With these injuries, proper diagnosis and treatment are essential for optimal recovery. Physical therapy often helps in rehabilitative efforts. Early detection of pelvic injuries can avert complications such as chronic pain or joint instability.
Osteoporosis and its Effects
Osteoporosis significantly impacts pelvic health, especially in women after menopause. This condition leads to decreased bone density, which raises the risk of fractures. The pelvis is a critical weight-bearing structure, and when weakened, it becomes susceptible to injuries. In fact, pelvic fractures are among the most serious consequences of osteoporosis and may result in long-term disability.
It’s important to understand:
- Risk Factors: Factors such as age, hormonal changes, and genetic predispositions can lead to an increase in osteoporosis risk.
- Preventive Measures: Engaging in weight-bearing exercises, ensuring adequate calcium and vitamin D intake, and avoiding smoking are effective strategies to mitigate osteoporosis risk.
Overall, orthopedic considerations surrounding the pelvis show the interconnection between bone health and mobility. By focusing on prevention and treatment of injuries and conditions like osteoporosis, healthcare practitioners can enhance the quality of life for affected individuals.
"Maintaining pelvic health through orthopedic awareness can lead to significant improvements in overall well-being."
Pelvic Imaging Techniques in Clinical Practice
Imaging plays a vital role in understanding the various conditions related to the pelvis. Accurate diagnosis is crucial for determining treatment plans and potential surgical interventions. Imaging techniques offer insights into structural abnormalities, injuries, and diseases affecting the pelvis.
The ability to visualize the pelvic region through non-invasive methods has greatly improved patient outcomes. Both X-ray, CT, and MRI techniques serve distinct purposes, each providing valuable information that assists healthcare professionals. This section will explore the strengths and limitations of these imaging modalities, focusing on their significance in clinical practice.
X-ray and CT Imaging
X-ray imaging is often the first step in evaluating pelvic conditions. It is quick, cost-effective, and readily available. X-rays are particularly beneficial for assessing fractures of the pelvic bones. They provide a two-dimensional view but may lack detail in more complex fractures and degenerative changes.
CT scans offer a more comprehensive assessment of the pelvis. They provide detailed cross-sectional images of the pelvic bones, soft tissues, and organs. This technique is effective for diagnosing tumors, infections, and places where more than one structure may be compromised. The speed of CT scanning can be useful in trauma situations where rapid assessment is necessary.
However, both X-ray and CT have considerations. The exposure to radiation is a concern. Careful evaluation of the necessity for these images should always be considered, especially in sensitive populations like pregnant women.
MRI Applications
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) has become increasingly essential in pelvic imaging. Unlike X-ray and CT, MRI uses magnetic fields to produce high-resolution images without radiation exposure. This is particularly beneficial when evaluating soft tissues such as muscles, ligaments, and organs, providing a detailed view of the pelvic floor structures.
MRI is invaluable in identifying conditions such as endometriosis, pelvic organ prolapse, and abnormal growths. Its utility extends to pre-operative planning, as it allows for clear visualization, thus aiding in the surgical approach and potential outcomes.
Despite the advantages, MRI has limitations, mainly its cost and longer duration compared to X-ray and CT. The need for patient cooperation on the duration of the scan can also pose challenges. In addition, certain metal implants may contraindicate the use of MRI.
Understanding these imaging techniques enhances clinical decision-making and individualized patient care for pelvic health issues. By evaluating the advantages and limitations of each imaging modality, healthcare professionals can choose the best approach for their patients.


In summary, imaging techniques, including X-ray, CT, and MRI, are pivotal in the assessment and management of pelvic conditions. Each method has its unique strengths and challenges. A thorough understanding of these modalities not only guides clinicians in diagnosis but also improves outcomes for women experiencing pelvic issues.
Surgical Interventions Related to the Pelvis
Surgical interventions concerning the pelvis play a critical role in addressing various health issues that can affect women. Understanding these procedures can aid healthcare professionals and patients alike in navigating treatment options. This section explores pelvic floor surgery and hip replacement procedures, both vital for improving quality of life.
Pelvic Floor Surgery
Pelvic floor surgery is essential for addressing conditions related to pelvic floor disorders, such as incontinence or pelvic organ prolapse. These disorders can significantly impact daily activities and overall well-being. Surgical interventions can restore pelvic structure and function, alleviating discomfort and improving patients’ quality of life.
The main types of pelvic floor surgery include:
- Colposuspension: This procedure raises the bladder neck to prevent urinary leakage.
- Vaginal mesh surgery: Used to treat prolapse, it provides support to weakened pelvic tissues.
Before proceeding with surgery, it is important to accomplish a thorough assessment, including a physical examination, imaging, or diagnostic tests. The decision must consider various factors, including the patient's overall health, age, and severity of symptoms. Additionally, understanding potential risks and complications is necessary. Common risks include infection, bleeding, and new symptoms like urgency or retention.
It’s also important to recognize postoperative care, as recovery periods vary significantly among patients. Active communication between the patient and healthcare providers serves to optimize outcomes and manage expectations.
Pelvic floor surgery can bring substantial relief and restore functionality, but it should always be approached with careful consideration of both benefits and risks.
Hip Replacement Procedures
Hip replacement procedures are relevant for women in terms of orthopedic health. Conditions like osteoarthritis or fractures may necessitate surgery when conservative treatments fail. The pelvis serves as a foundation for the hip joint, and any alteration in this area can directly affect mobility and pain levels.
The types of hip replacement surgeries include:
- Total Hip Replacement: The complete removal of damaged joint surfaces and replacement with artificial components.
- Partial Hip Replacement: Only the femoral head is replaced, preserving the acetabulum.
Typically, candidates for hip replacement experience significant pain and reduced functionality. Surgeons examine imaging studies, assess symptoms, and consider patient history to determine the appropriateness of surgery.
Postoperative care is essential. Patients often undergo rehabilitation to regain strength and mobility. This process may include physical therapy to enhance joint function and reduce stiffness.
Cultural and Social Perspectives on Pelvic Health
Cultural and social perspectives on pelvic health play a vital role in shaping women’s experiences, often influencing their health-seeking behaviors and treatment options. Understanding these perspectives is crucial for comprehending how women's health issues, particularly those related to the pelvis, are approached in various societies. This section examines cultural attitudes toward women's health and the social stigmas that often accompany pelvic health issues.
Cultural Attitudes Toward Women's Health
Cultural beliefs fundamentally affect how women view their bodies and their health. In some cultures, the pelvis is seen through a lens of strength and fertility, while in others, it may be stigmatized or associated with shame. The perception of pelvic health often correlates with broader views on gender roles and women's autonomy in healthcare.
For example, in cultures that emphasize reproductive roles, there might be a more positive attitude toward discussing issues such as childbirth and menstruation. Conversely, in societies where these topics are taboo, women may feel discouraged from seeking help for pelvic disorders, leading to adverse health outcomes.
The accessibility of education regarding pelvic health varies by region and cultural background. In some places, traditional practices coexist with modern medicine, which could either complement or conflict with how pelvic health is managed. Education is key to demystifying the pelvic area and promoting healthier attitudes toward women’s health.
Social Stigmas Surrounding Pelvic Issues
Social stigmas significantly affect women's willingness to openly discuss or seek treatment for pelvic health issues. Disorders such as incontinence, pelvic pain, or prolapse can carry significant stigma, leading women to feel embarrassed. This stigma can stem from misconceptions surrounding the pelvic area, often linked to sexual health or other intimate issues.
"Stigmatization can create barriers to care, preventing women from accessing necessary health services."
The repercussions of these stigmas are extensive. They can result in a delay in treatment, which can worsen health conditions. Societal norms about how women should talk about their bodies can further isolate those who experience pelvic health issues. For example, women may internalize feelings of shame or guilt, which can detrimentally affect their mental health as well as physical well-being.
To combat these stigmas, increased public awareness and education are essential. Initiatives that encourage open dialogue about pelvic health can significantly alter perceptions and support women in seeking assistance. Additionally, interdisciplinary approaches involving healthcare providers, educators, and community leaders may aid in breaking down these societal barriers.
In summary, cultural and social perspectives are crucial in understanding pelvic health. Acknowledging and addressing these attitudes can help improve women's access to care and enhance their overall health outcomes.
Future Directions in Pelvic Research
Research into the pelvis, particularly its roles in women's health, is an evolving field. Understanding the pelvis is essential not only for anatomical knowledge but also for addressing various health issues that affect women. Current trends focus on better comprehension of pelvic disorders, improved treatment modalities, and the integration of advanced technologies. Exploring the future directions of pelvic research is vital as it can lead to innovative solutions to long-standing issues and enhance the quality of life for many.
Emerging Studies and Technologies
The landscape of pelvic research is rapidly changing with the advent of new studies and technologies. Here are some noteworthy elements emerging from this field:
- Genomic Insights: Recent studies focus on how genetics influence pelvic disorders. Knowledge of genetic markers may lead to personalized treatment strategies.
- Biomechanical Analysis: Research incorporating advanced biomechanics is helping to understand how pelvic anatomy affects movement and strength. This can be particularly beneficial in sports medicine.
- Imaging Advances: High-resolution imaging techniques such as 3D ultrasound and MRI are becoming more common. These technologies allow for a non-invasive exploration of pelvic structures and can help in precise diagnosis.
- Artificial Intelligence: AI applications are emerging in pelvic research. They assist in analyzing large data sets for better understanding and prediction of pelvic health issues.
- Telehealth Innovations: The rise of telemedicine permits remote consultations and monitoring, improving access to pelvic health specialists.
Implementing these technologies can not only improve research outcomes but also translate into better clinical practices.
Interdisciplinary Approaches to Pelvic Health
The future of pelvic health research increasingly relies on an interdisciplinary approach. Collaborations among disciplines can address complex health issues more effectively. Here are some important aspects:
- Integration of Disciplines: Combining insights from gynecology, urology, orthopedics, and physical therapy leads to more holistic treatment plans.
- Community Engagement: Involving community health workers in pelvic health can improve awareness and education. This is crucial for addressing social stigmas surrounding pelvic issues.
- Policy and Advocacy: Research should also intertwine with public health policies to influence funding and support for women's health initiatives.
"An interdisciplinary approach enhances our understanding, leading to better strategies for managing pelvic health."
- Research Partnerships: Collaboration between academic institutions and healthcare facilities is essential for translating findings into practical applications.
Understanding pelvic health through interdisciplinary methods can enhance the effectiveness of treatment and broaden the understanding of its complexities.
The future of pelvic research is hopeful and promising, driven by technological advances and collaborative practices. Emphasizing these aspects can lead to substantial improvements in women's health outcomes and overall well-being.







